Copyright (c) Hyperion Entertainment and contributors.
AmigaOS Manual: Utilities: Difference between revisions
Added the parameter descriptions. |
Added screenshot |
||
| Line 1,031: | Line 1,031: | ||
RawDisk reads or writes a given number of cylinders or blocks to or from a disk, transferring the data to or from a named file. The data is read or written in raw format, i.e. the disk filesystem (if any) is ignored and data is addressed absolutely. |
RawDisk reads or writes a given number of cylinders or blocks to or from a disk, transferring the data to or from a named file. The data is read or written in raw format, i.e. the disk filesystem (if any) is ignored and data is addressed absolutely. |
||
[[File:WorkbenchUtilitiesFigRawDisk.png|frame|left|RawDisk Window]] |
|||
<div style="clear: both"></div> |
|||
The utility can be used on any disk present in the DOS List, i.e. mounted. It can be run from Workbench by clicking the icon or from a Shell. |
The utility can be used on any disk present in the DOS List, i.e. mounted. It can be run from Workbench by clicking the icon or from a Shell. |
||
Revision as of 14:51, 31 December 2020
The Utilities drawer contains programs that are helpful, but not necessary for working with your Amiga.
AmiGS
AmiGS is a viewing and printing utility for postscript, EPS, and PDF documents.
Tool Types
AmiGS supports the following Tool Types:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| WINDOWBOX=<left>/<top>/<width>/<height> | This tool type allows you to define AmiGS window position and dimensions. |
| PUBSCREEN=<public screen> | Name of the public screen. AmiGS will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this tool type. |
Shell Usage
- Format
- AMIGS [FILE <file name>] [PAGE <page number>] [PAGENAME <page name>] [ZOOM <zoom factor>] [PUBSCREEN <public screen name>] [FULLSCREEN]
- Template
- FILE,PAGE/N,PAGENAME/K,ZOOM/K,PUBSCREEN/K,FULLSCREEN/S
ARexx Interface
AmiGS has an ARexx interface which allows other programs to control AmiGS while it is running. AmiGS's ARexx port name is AMIGS.<slot #>, where <slot #> is the ARexx port slot. When you have one AmiGS running, its ARexx port is AMIGS.1. The other instance of AmiGS has a port named AMIGS.2, the third instance AMIGS.3 and so on.
AmiGS upports the following ARexx commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| GETDEFAULTID | Returns the default document ID in the ARexx variable RESULT.
AmiGS creates a unique ID number for each opened document. The first opened document will get this ID number. AmiGS generates a new document ID by adding 1 to the last used ID number. Thus the second document's ID number will be 2, third's 3, and so on. When you close a document, its ID number won't be reused. |
| QUIT | Quits the application. |
| OPEN [<file name>] | Opens the named file in a new window or if the file name is not supplied, displays a file requester for selecting a file. |
| CLOSE <document id> | Closes an open document using the AmiGS's internal document ID number. |
| FIRSTPAGE <document id> | Displays the first page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| LASTPAGE <document id> | Displays the last page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| PREVPAGE <document id> | Displays the previous page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| NEXTPAGE <document id> | Displays the next page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| GOTOPAGE <document id> <page number> | Displays the requested page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
AmiPDF
AmiPDF is a PDF document viewer. It can also be used for converting PDF documents to text files and PostScript files.
Tool Types
AmiPDF supports the following Tool Types:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| WINDOWBOX=<left>/<top>/<width>/<height> | This tool type allows you to define AmiPDF window position and dimensions. |
| PUBSCREEN=<public screen> | Name of the public screen. AmiPDF will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this tool type. |
Shell Usage
- Format
- AMIPDF [FILE <filename>] [PAGE <page number>] [PAGENAME <page name>] [OWNERPASS <password>] [USERPASS <password>] [ZOOM <zoom factor>] [PUBSCREEN <public screen name>] [FULLSCREEN] [PAPERSIZE <paper size>] [PAPERWIDTH <paper width>] [PAPERHEIGHT <paper height>] [PSLEVEL1] [TEXTENCODING <encoding> ] [QUIET]
- Template
- FILE,PAGE/N,PAGENAME/K,OWNERPASS/K,USERPASS/K,ZOOM/K,PUBSCREEN/K,FULLSCREEN/S,PAPERSIZE=PS/K,PAPERWIDTH=PW/K,PAPERHEIGHT=PH/K,PSLEVEL1/S,TEXTENCODING=TE/K,QUIET/S
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| FILE | Name of the PDF file to open. |
| PAGE | Page number. Open the PDF document from the specified page. |
| PAGENAME | Like PAGE except you can use page names instead of page numbers. |
| OWNERPASS | Document's owner password. Providing this will bypass all security restrictions. |
| USERPASS | Document's user password. As a minimum this will unlock the read protection. |
| ZOOM | Initial zoom factor. Percentage value. |
| PUBSCREEN | Name of the public screen. AmiPDF will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this argument. |
| FULLSCREEN | Display the PDF document using the full-screen mode. |
| PAPERSIZE | Paper size: LETTER, LEGAL, A4, or A3. |
| PAPERWIDTH | Set the paper width in points. |
| PAPERHEIGHT | Set the paper height in points. |
| PSLEVEL1 | Generates Level 1 PostScript. The resulting PostScript file will be significantly larger (if it contains images), but will print on Level 1 printers. This also converts all images to black and white.
By default AmiPDF generates Level 2 PostScript. |
| TEXTENCODING | Sets the encoding to use for text output. |
| QUIET | Don't print any messages or errors. |
ARexx Interface
AmiPDF has an ARexx interface which allows other programs to control AmiPDF while it is running. AmiPDF's ARexx port name is AMIPDF.<slot #>, where <slot #> is the ARexx port slot. When you have one AmiPDF running, its ARexx port is AMIPDF.1. The other instance of AmiPDF has a port named AMIPDF.2, the third instance AMIPDF.3 and so on.
AmiPDF supports the following ARexx commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| GETDEFAULTID | Returns the default document ID in the ARexx variable RESULT.
AmiPDF creates a unique ID number for each opened document. The first opened PDF document will get this ID number. AmiPDF generates a new document ID by adding 1 to the last used ID number. Thus the second document's ID number will be 2, third's 3, and so on. When you close a document, its ID number won't be reused. |
| QUIT | Quits the application. |
| OPEN [<pdf file>] | Opens the named PDF file in a new window or if the file name is not supplied, displays a file requester for selecting a file. |
| CLOSE <document id> | Closes an open PDF document using the AmiPDF's internal document ID number. |
| FIRSTPAGE <document id> | Displays the first page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| LASTPAGE <document id> | Displays the last page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| PREVPAGE <document id> | Displays the previous page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| NEXTPAGE <document id> | Displays the next page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| GOTOPAGE <document id> <page number> | Displays the requested page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
BRU
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
ARexx Interface
Calculator
The Calculator is a standard four-function calculator for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing. Opening the Calculator icon activates it.
The calculator works like any standard calculator. The buttons on the calculator are gadgets. The numbered gadgets represent the digits 0 through 9. The non-numerical gadgets represent:
| CA | Clear all previous entries. Resets the calculator to 0. |
| CE | Clear the current entry. |
| X | Multiply. |
| / | Divide. |
| + | Add. |
| - | Subtract. |
| . | Decimal point. |
| « | Delete the last digit entered. |
| ± | Change the sign of the current entry. Positive numbers become negative; negative numbers become positive. |
| = | Display the result of the operation. |
To press a button, select the gadget with the mouse or press the corresponding key on the keyboard. You can use either the keyboard or numeric keypad keys. Return and the keypad Enter key are equivalent to the equals (=) button. The left arrow key is equivalent to the («) button.
The calculator displays a message for Overflow and Divide By Zero errors.
Select the close gadget to exit the Calculator.
The calculator has three menus: the Project menu, the Edit menu, and the Windows menu.
On the Project menu:
| Clear Entry | Clears the current entry only. |
| Clear All | Clears all entries and resets the display to zero. |
| Quit | Closes off the calculator. |
On the Edit menu:
| Cut | Copies and clears the current entry to the Clipboard. |
| Copy | Copies the current entry to the Clipboard without clearing the area. |
| Paste | Place the current Clipboard contents into the calculator. |
Show Tape is the only Window menu option. It displays a window showing the calculator entries and results. Show Tape can also be copied, but since it does not have a menu, use drag-select and Amiga+C to copy its contents to the Clipboard.
Tool Types
Calculator supports the following Tool Types:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| PUBSCREEN=<public screen name> | Name of the public screen. Calculator will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this tool type. |
| TAPE=<window specification> | Defines a custom tape window. |
| GUIMODE=SIMPLE|EXTENDED | Selects which user interface mode Calculator will use. SIMPLE opens a basic calculator while EXTENDED opens a scientific calculator. |
Shell Usage
- Format
- CALCULATOR [PUBSCREEN <public screen name>] [GUIMODE SIMPLE|EXTENDED] [TAPE <window specification>] [COMPUTE <expression>]
- Template
- PUBSCREEN,GUIMODE/K,TAPE/K,COMPUTE/K/F
ARexx Interface
Calculator has no ARexx interface.
Clock
Clock displays the time and date on your Workbench screen. It can also be used as an alarm clock to signal you at a specified time.
When you open the Clock icon, a window with a round (analog) clock face appears. If the time Shown is incorrect, use the Time editor in the Prefs drawer, described in Chapter 5, to set the correct time.
Clock Menus
Clock has two menus for changing the display and settings: Project and Settings.
The Project menu contains the following items:
| Analog | Displays the round Clock face. Analog is the default; its window size can be changed. |
| Digital | Displays a digital (numeric) clock the height of the title bar using your screen font. |
| Quit | Closes the Clock. |
The Settings menu contains the following items:
| Date | Displays the date beneath the analog clock. The date and time are alternately displayed on the digital clock. Date off is the default. |
| Seconds | Displays the time with a sweep second hand on the analog clock. The default setting shows no seconds. The Display Seconds item is overridden by the Digital Format setting when using the digital clock. |
| Digital Format | Displays the time in a 12 or 24 hour format, with or without seconds, for the digital clock only. |
| Alarm | Allows you to turn the alarm on or off. A checkmark indicates that the alarm is on. |
| Set Alarm | Allows you to set the time for the alarm to signal you. Because the signal is a short audible tone, you must have audio output on your Amiga to use this feature. |
| Save Settings | Saves your Clock settings. Each time you run the Clock program it opens with these settings until you change them. |
To set the alarm:
- Choose the Set Alarm menu item.
- Change the time setting by dragging the hour and minute sliders to the right to increase the value or the left to decrease the value until the correct time is displayed.
- When the requester displays the desired alarm time, select the Use gadget. This automatically turns the alarm on, as indicated by the checkmark next to the Alarm menu item. Select the Cancel gadget to restore the previous alarm setting and exit.
The alarm remains on and beeps at the same time each day until you deselect Alarm or close the Clock. The Clock must be running for the alarm to work. The next time you open the Clock, the alarm must be reset.
Tool Types
Tool Types in the Clock icon's Information window allow you to save the menu, size, and position settings on the Clock. The Clock's Tool Types are the same as its keywords in AmigaDOS.
Shell Usage
- Format
- CLOCK [DIGITAL] [<left>] [<top>] [<width>] [<height>] [24HOUR] [SECONDS] [DATE] [<format>] [<public screen>]
- Template
- DIGITAL/S,LEFT/N,TOP/N,WIDTH/N,HEIGHT/N,24HOUR/S,SECONDS/S,DATE/S,FORMAT/N,PUBSCREEN/K
ARexx Interface
Clock has no ARexx interface.
More
More displays ASCII text filers on the Workbench screen. More does not have an icon, although it resides in the Utilities drawer. More has been superseded by the MultiView program, but is retained for compatibility with files that use More as their Default Tool.
The following key sequences can be used to move through the More display and to get help for using More:
| Space bar or down arrow | Displays the next page. |
| Backspace or up arrow | Displays the previous page. |
| H | Help (displays a list similar to this one). |
When the last page of the display is reached, an End of File message is displayed at the bottom of the screen. Press the space bar at this point or click the close gadget at any time to exit More.
Tool Types
(none)
Shell Usage
- Format
- MORE <file>
- Template
- FILE
ARexx Interface
More has no ARexx interface.
GraphicDump
GraphicDump prints (or dumps) entire screens, including menus and icons, just as they appear on your monitor. Your printer must be capable of printing graphic images. (Most printers can print GraphicDump output.)
Before using GraphicDump, make sure the settings in the Printer, PrinterPS, and PrinterGfx Preferences editors are appropriate for your printer. You can specify the dimensions of the printout with the Limits setting in the PrinterGfx editor. Otherwise, the printout is the full width allowed by the printer.
To use GraphicDump, double-click on its icon. After a ten second delay the front-most screen image is sent to the printer. The mouse pointer is not printed.
Tool Types
GraphicDump supports a SIZE Tool Type. The acceptable arguments for SIZE and the resulting size of the printout are:
| SIZE=tiny | 1/4 the total width allowed by the printer. |
| SIZE=small | 1/2 the total width allowed by the printer. |
| SIZE=medium | 3/4 the total width allowed by the printer. |
| SIZE=large | Full width allowed by the printer (default). |
The height of the printout maintains the perspective of the screen. The Limits Type gadget in the PrinterGfx editor must be set to Ignore for GraphicDump, or else the size of the printout is determined by the Limits setting.
To set specific dimensions in a Tool Type, use:
SIZE=<xdots>:<ydots>
Substitute the width, in number of printer dots, for the <xdots> argument and the height for the <ydots> argument.
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
GraphicDump has no ARexx interface.
IconEdit
IconEdit personalizes your Workbench by changing the appearance of existing icons and creating new ones.
The window shown in Figure 10-2 appears when you open the IconEdit icon.
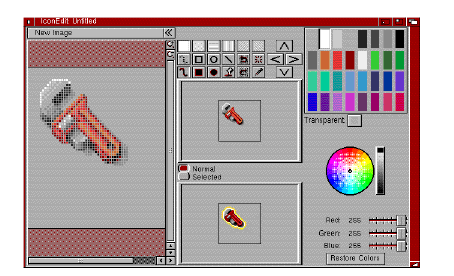
Draw and edit icons in the magnified view box of the IconEdit window. The Normal and Selected view boxes show the icon images at actual size. Several gadgets in the window draw squares, circles, and straight lines, giving you more control over your drawing.
There are three subwindows in IconEdit: the Normal and Selected view boxes and the Magnified View Box, which fills most of the window. Each of these is an AppWindow into which you can drag an icon to load it, rather than using menus. (AppWindows are described in Chapter 3.) Clicking in the Normal view box displays the selected image of the icon as long as you hold down the selection button.
Color Selection Gadget
The Color Selection gadget lets you select a color for drawing. In addition to the standard method for selecting a color by pointing to it and clicking the selection button, this gadget allows you to choose two-color patterns. The patterns are used with the Fill, filled Circle, and filled Box gadgets.
In order to use fill patterns you need to select the first color by left-clicking on it. After that keep the Shift key depressed and select the second color. The gadget bar with the different fill patterns will change its appearance accordingly, giving a simple preview on the two-color patterns.
Below the color selection gadget there is the Transparent gadget. Selecting a color from the palette and clicking on Transparent" afterward will make this color invisible" when the icon is saved to disk. Clicking on the Transparent gadget a second time using the same color will deactivate transparency.
Magnified View Box
Use the mouse to draw your icon in this box. Click the selection button to display a pixel of the selected color. Hold down the selection button to draw while moving the mouse.
The pointer turns into cross hairs when it is in the magnified view box. The new pixels appear a the center of the cross hairs. Pixel coordinates (relative to the upper left corner) appear in the middle of the IconEdit window below the title bar to show the position of the crosshair.
To load an existing icon into IconEdit, drag the icon into the magnified view box.
Fill pattern Gadgets
These gadgets allow you to select the fill pattern to be used with filled rectangles, filled circles and the flood fill tool.
Freehand Gadget
The Freehand gadget lets you quickly draw unstructured shapes. If you select this gadget and then draw in the magnified view box, the pixels fill in as the mouse passes over them. However, you may not get a continuous line and some pixels may not be filled in. Use this gadget to sketch an icon that you intend to fill in the details on later.
Continuous Freehand Gadget
The Continuous Freehand gadget is similar to the freehand gadget, except that it produces a continuous line. When drawing continuous lines, there is a delay before the display catches up with your movement.
Circle Gadget
To draw a circle or oval:
- Select the circle gadget.
- Point inside the magnified box at the point where you want the center of the circle, hold down the selection button, and move the mouse.
- Release the selection button when you reach the correct size and shape.
If you keep the Shift key depressed while drawing the circle, a true circle, rather than an ellipse, will be drawn.
Filled Circle Gadget
Follow the steps for drawing normal circles to draw a filled circle or ellipse, using the current fill pattern.
Box Gadget
To draw a box:
- Select the box gadget.
- Point inside the magnified boy at the point where you want a corner of the box, hold down the selection button, and move the mouse.
- Release the selection button when the box is the correct size and shape.
If you keep the Shift key depressed while drawing the box, a true square will be drawn instead.
To draw a three-dimensional box, similar in appearance to the Workbench gadgets, hold down an Alt key while drawing a box outline. The left and top border of the box will then be drawn using the current color while the right and bottom borders will be drawn using the color currently selected as the second color for fill patterns.
Filled Box Gadget
Follow the steps for drawing a normal box in order to draw a filled box or square using the current fill pattern.
Line Gadget
To draw a straight line:
- Select the line gadget.
- Position the mouse where you want the line to start.
- Hold down the selection button.
- Move the mouse to the line ending position.
- Release the selection button.
Fill Gadget
Use the fill gadget to fill an area of the magnified view box with the selected color. Select the fill gadget, then click within the area you want to change to the same color as the dot under the crosshair.
| Note |
|---|
| The fill gadget does not fill a patterned area. However, solid areas can be filled with one of the fill patterns, if selected. |
Undo
Select Undo to cancel the last mouse action performed in the magnified view box. Undo acts as a toggle switch; selecting it again undoes the Undo.
Redo
Select Redo to cancel the last undo action, effectively restoring the state the magnified view box was in before calling undo.
Clear
Select the Clear gadget to erase the contents of the magnified view box. The magnified view box fills with the currently selected color.
Normal/Selected Radio Buttons
The Normal and Selected radio buttons switch between unselected and selected images for an icon. The normal image is how an unselected icon looks. The selected image is how a dual-image icon looks after you have clicked on it.
When the Normal radio button is selected, any image drawn in the magnified view box appears in the normal view box at the top of the window.
When the Selected radio button is used, you can create the image that appears when the icon is selected. You can only use this radio button when the Image menu item is chosen from the Highlight menu. Any image created appears in the selected view box.
Arrows
The arrows let you shift your image. Clicking on an arrow moves the image in the magnified view in the direction of the arrow. Use these arrows to control the placement of your image within the box surrounding the finished icon.
| Note |
|---|
| Any part of the image that is moved off the edge of the magnified view box is lost. |
Keyboard shortcut: Press the corresponding arrow key to move the image.
Project Menu
The items in the Project menu let you open and save icon files.
| New | Loads the default icon for the currently chosen type of icon. (The type of icon is determined by the Type menu.) Any changes in the window that have not been saved produce a requester asking if you want to save them. |
| Open | Opens an existing icon file. A requester appears for entering the name of the file. Only the names of drawers and .info files appear in the IconEdit Open file requester. |
| Revert | Restores the icon to the state it was in when it was last saved to disk, removing all changes that had been made since then. If the icon has not been previously saved, this menu item will be ghosted. |
| Save | Saves an existing icon file, overwriting any file with the same name. In this case the previous icon is lost. |
| Save As | Allows you to specify a file name for saving the current image. A requester lets you enter the destination for the edited icon. Use Save As to prevent overwriting an existing icon file. |
| Save As Default Icon | Saves the current image as the default icon for the currently selected icon type. This image is used for any new icon or pseudo-icon of that type created, including those made with the New menu item in the IconEdit Project menu. For example, if you create a drawer icon and then choose Save As Default Icon, that icon is used to represent drawers when you choose the Show All Files menu item. |
| Quit | Exits the IconEdit program. If you have not saved the current image, a requester asks if you want to save the image before exiting IconEdit. |
Edit Menu
The items in the Edit menu allow you to use the Amiga`s Clipboard to import IFF ILBM clips that were created with other programs.
| Cut | Deletes the image in the magnified view box and copies it to the Clipboard. |
| Copy | Copies the image in the magnified view box to the Clipboard. |
| Paste | Copies any image in the Clipboard to the magnified view box, replacing the current contents. |
| Erase | Erases any image in the magnified view box. You can erase everything or save before erasing. |
| Undo | Has the same function as the corresponding gadget. |
| Redo | Has the same function as the corresponding gadget. |
| Open Clip | Copies an existing IFF file into the Clipboard. A requester asks for the name of the file to open. You can then Paste the file into IconEdit. |
| Save Clip As | Saves the current contents in the Clipboard to a specified file. |
| Show Clip | Displays the current contents in the Clipboard using the MultiView program. If the MultiView program is unavailable, Show Clip cannot work. |
Type Menu
The items in the Type menu let you specify the type of icon changed or created.
| Disk | Represents the disk icons appearing in the Workbench window. |
| Drawer | Represents the drawer icons appearing in a disk window, such as the Utilities or Tools drawer. |
| Tool | Represents a tool, such as the Calculator, Clock, or IconEdit program. |
| Project | Represents a project, a file that has been created by a tool, such as any of the icons in the drawers of the Storage directory. |
| Garbage | Represents the Trashcan drawer. |
Highlight Menu
The items in the Highlight menu let you determine how an icon appears when it is selected.
| Complement | Highlights the entire icon, including the background of the box surrounding the icon. For example, if you are using the default Workbench colors and the icon is surrounding by a field of grey, the grey becomes blue when the icon is selected. This option is only available in old icons" mode. |
| Backfill | Highlights the icon, but not the background of the box. For example, if you are using the default Workbench colors and the icon is surrounded by a field of grey, the grey remains the same when the icon is selected. This option is also only available in old icon" mode. |
| Image | Allows an entirely different image for the selected icon (a dual image icon). For example, the drawer icons on the Workbench are dual image. When you select a drawer, a new image of an open drawer appears. |
Images Menu
The items in the Images menu let you manipulate the images in the normal and selected view boxes and import IFF images created with other graphics programs.
| Exchange | Swaps the images that appear in the normal view and the selected view. |
| Copy | Copy is dependent on the selected radio button. If Normal is used, the image in the normal view is copied to the selected view. If Selected is used, the image in the selected view is copied to the normal view. |
| Use Template | Loads a template icon into the magnified view box on which you can use as the foundation for creating a new icon. |
| Darken | The icon's colors will be darkened. |
| Load | Loads previously saved images, without changing the name of the icon being edited. When you point to the Load menu item, a submenu (described below) appears. |
| Save Image | Saves an image as a standard IFF ILBM brush, rather than an icon. |
| Restore | Returns the IconEdit window to its state prior to opening the window or selecting New or Open. |
The available Load submenu items are:
| Image | Allows you to load an image data type file created by another program as either the normal or selected view, depending on which radio button is selected. When you choose an item from the submenu, a requester asks you to specify the file to be loaded. You must specify the correct drawer and file name. |
| Normal Image | Loads the unselected image of the specified icon into the normal or selected view box, depending on which radio button is selected. (This is equivalent to dragging an icon into one of the boxes.) |
| Selected Image | Loads the selected image of the specified icon into the normal or selected view box, depending on which radio button is selected. |
| Both Images | Loads both the normal and selected images of the specified icon into the appropriate view boxes. |
Extras Menu
The items in the Extras menu control additional convenience features of IconEdit.
| Larger Sketchboard | Increases the drawing area IconEdit provides. Any existing elemens will retain their distance to the top and left edges of the sketchboard. |
| Smaller Sketchboard | Decreases the drawing area IconEdit provides, removing space from the bottom and the left of the sketchboard. If this would result in the image being truncated, IconEdit will ask for confirmation before cropping the image. |
| Minimal Sketchboard | Decreases the drawing area IconEdit provides, to the effect that all blank space to the right and bottom of the current image will be removed. |
| Auto TopLeft | Moves the image to the upper left corner of the magnified view box. |
| Add Glow | Automatically adds a glow effect to the icons, just like the standard OS3.5 icons have. |
| Borderless | If this menu item is active, the icon will be saved and displayed without a border, regardless of the global border settings from the Workbench preferences. |
Settings Menu
The items in the Settings menu allow you to save various IconEdit options.
| Use Grid? | Use Grid? Displays each pixel in the magnified view box distinctly, with the background color surrounding it. When Use Grid? Is not chosen, the pixels blend together smoothly. The default is for the grid to be on. |
| Save Optimized? | Choosing this option will cause the transparency color to be assigned the color number zero (if possible) and remove all colors from the icon`s palette that are not actually used. |
| Create Icons? | Create Icons? Saves an icon for the IFF brush file created by the Save Image menu option. If Create Icons? Is not chosen, no icon is saved. The default is for icons to be saved. |
| Slider Color Model | This submenu controls whether the RGB or HSB color model will be used for the color sliders. |
| Save Settings | Save Settings saves all of the current IconEdit settings, including the size and position of the IconEdit window, the file requesters, and all of the menu item settings. |
Tool Types
IconEdit supports the following Tool Types:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| PUBSCREEN | Names the public screen on which IconEdit is supposed to open its window. |
| TEMPLATE | Path to the icons to be loaded when calling the Use Template" menu item. |
| HSB | Use the HSB color model for the color sliders. |
| OPTIMIZE | Optimize the icon palette when saving icons. |
| CLIPUNIT=<n> | Specifies the Clipboard unit to use. The default is 0. |
| XMAG=<n> | Enlarges the width of the magnified view box. XMAG accepts a number from 4 to 16. The default is 4. |
| YMAG=<n> | Enlarges the height of the magnified view box. YMAG accepts a number from 4 to 16. The default is 4. |
| LEFTEDGE=<n> | Specifies where to place the left edge of the editor window. |
| TOPEDGE=<n> | Specifies where to place the top edge of the editor window. |
| SHOWCLIP=<path> | Specifies the complete path to the utility used to display the Clipboard. The default is SYS:Utilities/MultiView. |
| NOICONS | Disable the ability to create icons when saving support files, such as when saving a file as an IFF brush. |
| NOGRID | Disables the use of the grid in the magnified view box. |
| ICONDRAWER=<path> | Specifies the default drawer used by the file requesters that appear when the Open and Save As menu items in the Project menu are chosen. |
| ILBMDRAWER=<path> | Specifies the default drawer used by the file requesters that appear when the Load and Save menu items in the Images menu are chosen. |
| CLIPDRAWER=<path> | Specifies the default drawer used by the file requesters that appear when the Open Clip and Save As Clip menu items in the Edit menu are chosen. |
| ALTDRAWER=<path> | Specifies the default drawer used by the file requesters that appear when the Load menu item in the Images menu is chosen. |
InitPrinter
InitPrinter sends the printer options specified in the Printer Preferences and PrinterGfx Preferences editors to the printer. It initializes your printer and loads it with the new or changed specifications when you turn on the printer and double-click on the InitPrinter icon.
Your printer resets automatically when it receives and processes initialization information on first access during a session. If you turn the printer off, you might need to use InitPrinter to reinitialize it.
Tool Types
(none)
Shell Usage
- Format
- INITPRINTER
- Template
- (none)
ARexx Interface
InitPrinter has no ARexx interface.
Installation Utility
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
ARexx Interface
Installer
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- INSTALLER <script> [<app name>] [<min user>] [<def user>] [<log file>] [<language>] [NOPRETEND] [NOLOG] [NOPRINT]
- Template
- SCRIPT/A,APPNAME,MINUSER,DEFUSER,LOGFILE,LANGUAGE,NOPRETEND/S,NOLOG/S,NOPRINT/S
ARexx Interface
KeyShow
The KeyShow program shows the current keyboard type layout on your Amiga. Opening the KeyShow icon displays the keyboard layout as selected in the Input Preferences editor. The default American keyboard layout is illustrated in the figure below.
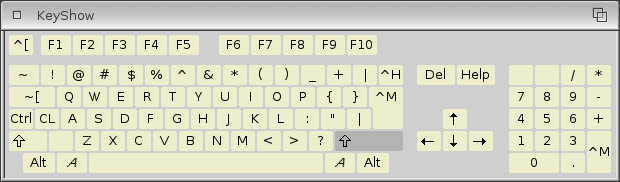
The initial display shows the characters that appear when a single key is pressed. For example, the Q key shows a lower case q. However, when you press a qualifier key with a character key, you can get different output. For KeyShow the acceptable qualifier keys are Ctrl, Shift and both Alt keys.
To see the characters that are output when a qualifier key is pressed simultaneously with a character key:
- Select any of the qualifier keys that appear in the KeyShow window. That qualifier key is highlighted.
- The KeyShow display changes to indicate the output that you get if you press the selected qualifier key along with a character key. You can select any combination of qualifiers and the display changes accordingly.
- Select the qualifier key again to return it to its unpressed state.
Keyboard shortcut: Instead of pointing to the qualifier key in the display, you can press the corresponding key on the keyboard. The following list is a guide to interpreting the KeyShow display:
- Qualifier keys not currently pressed are shown in the Workbench background color (normally grey). For example, when you first open the KeyShow window, Ctrl, Shift, and Alt appear in grey. This is because KeyShow is not using those keys in the initial display.
- Dead keys are shown in the Workbench highlight color (normally blue). A dead key is one that, in combination with an Alt key, modifies the output of the key pressed immediately afterward. For example, on the USA keyboard, the Alt+G combination is a dead key representing the grave accent. If you press Alt+G, then press E, you superimpose the accent symbol over the e (è).
- Bold-italics indicate that a key can be used in conjunction with a dead key. In the previous example, E can be modified by a dead key. However, not all bold-italic keys are affected by all dead keys. For example, n responds only to the Alt+J dead key. The final character must exist in the Amiga character set to be available through a dead key.
- $$ indicates that it takes more than one character to define the key.
- If a character is preceded by a tilde (~) or a caret (^), it is a control character.
- Blank keys are undefined for the currently selected qualifiers.
Tool Types
(none)
Shell Usage
- Format
- KEYSHOW
- Template
- (none)
ARexx Interface
KeyShow has no ARexx interface.
MEmacs
MEmacs (MicroEmacs) is a screen-oriented text editor. A text editor works the same as a word processor, but it does not support style formatting options. MEmacs is described in detail in the AmigaDOS User's Guide .
MultiView
MultiView lets you view files, including picture files, text files, AmigaGuide help files, sound files, and animated graphics files. It can display any type of file for which there is a data type file in DEVS:DataTypes. For more information on the data types used by MultiView, see page 4-28.
MultiView uses a standard file requester for loading files. You can load files into MultiView using the file requester provided or, because the MultiView window is an AppWindow, you can drag icons onto MultiView to load them.
When you loaded a standard Amiga sampled sound file into MultiView, clicking on the file's icon plays the sampled sound if your Amiga or monitor has speakers.
When you load an animated file into MultiView, the window or screen on which the animation is displayed has a control panel for manipulating the display. The control panel gadgets allow you to start and stop the animation and move forward or backward through it. This screen is illustrated in the figure below.
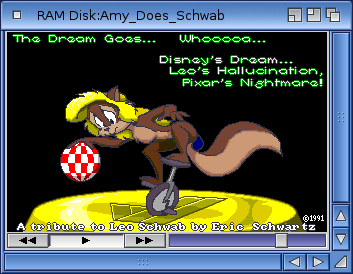
MultiView has four menus: Project, Edit, Windows, and Settings.
Project Menu
| Open | Brings up a file requester to allow you to choose another file to display. |
| Save As | Saves object as ILBM or text files. |
| Prints selected blocks or files. | |
| About | Shows the MultiView release information and the type of document being viewed. |
| Quit | Quits MultiView. |
Edit Menu
| Mark | Turns on the block selection cursor and lets you select a block. (This is only available for picture files.) |
| Copy | Copies selected block to the Clipboard and deselects the block. If no block is selected, copies the whole file. |
| Select All | Selects the whole file. |
| Clear Selected | Clears the selected block or file without copying or printing. |
Windows Menu
| Use Separate Screen | Toggles between displaying the file on its own screen and in a window on the Workbench screen. |
| Minimize | Make the window as small as it can be. |
| Normal | Sizes the window to the contents size. |
| Maximize | Makes the window the same size as the screen. |
Settings Menu
| Save As Defaults | Saves the size, position, and location of the window for future use. |
Tool Types
MultiView supports the following Tool Types:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| CLIPBOARD | View The Clipboard instead of the file. |
| CLIPUNIT=<number> | Specify the Clipboard unit to use when using the CLIPBOARD keyword. The range is 0 to 255; the default is 0. |
| SCREEN | Indicate that you want the object to appear on its own screen, using the environment specified by the object. For example, if an ILBM was Low Res, then the screen would match. |
| PUBSCREEN=<name> | Indicate that you want the window to open on the named public screen. |
| FONTNAME=<name> | Font to use when viewing text objects. Note that the .font extension must be left off. |
| FONTSIZE=<number> | Font size to use when viewing text objects. |
| BOOKMARK | Go to the object and position specified by the bookmark. |
| BACKDROP | Indicate that the window should be a backdrop window. |
| WINDOW | Open the MultiView window on the Workbench screen without an object so that items can be dragged into it. |
| PORTNAME=<ARexx port name> | Allows you to specify an ARexx port name when you run MultiView. This name allows you to refer to a particular MultiView display from within an ARexx script. If no name is specified, each MultiView invocation is given a default name. |
For more information on using MultiView with ARexx, see the AmigaDOS User's Guide.
NotePad
Missing description.
NotePad Menus
Missing description.
PartitionWizard
Missing description.
PartitionWizard Menus
Missing description.
PlayCD
PlayCD acts as a user interface for the audio CD playback functionality offered by a CD-ROM drive. The CD-ROM drive in question must comply to the SCSI-2 standard and thus support at least a subset of the audio control commands defined for CD-ROM drives.
Starting the program
When the program is launched, it will attempt to configure itself. This involves figuring out which device driver and which device unit to use for audio playback. This information is usually stored in the program's icon, but it can also provided on the command line. The names of the command line options and the tool types are the same. The following options are supported:
- DOSDEV
- If there already is a filing system mounted on the CD-ROM drive to use for audio playback, the easiest way to tell PlayCD which device it should use is to provide that filing system's name. PlayCD will try to figure out which device and unit that filing system is bound to and use the resulting information.
- Example:
PlayCD CD0: PlayCD dosdev CD2:
| Note |
|---|
| That this type of configuration may not work with all CD-ROM filing systems. |
- DEVICE
- Use this option to provide the name of the device driver the CD-ROM drive to use for playback responds to.
- Example:
PlayCD device=scsi.device
- Default for this option is "scsi.device" .
- UNIT
- This option works in conjunction with the "DEVICE" parameter. Both the device name and the unit number specified define the interface the PlayCD program should use to address the CD-ROM drive.
- Example:
PlayCD unit=5
- Default for this option is "2".
- SKIP
- The PlayCD user interface sports a slider which controls and displays the current play index. Attached to this slider are two buttons which perform fast forward" and rewind" functionality. Pressign any of these two buttons will cause playback to skip a few seconds. The SKIP" option is for configuring the number of seconds to skip.
- Example:
PlayCD skip=2
- Default for this option is 1", i.e. clicking on the buttons will skip one second each.
- PEEKTIME
- PlayCD queries the CD-ROM drive in regular intervals to find out whether the CD was changed or how far playback has progressed. The length of these intervals is configured with the PEEKTIME" option. The peek time is specified in microseconds, i.e. one millionth part of a second.
- Example:
PlayCD peektime=500000
- Default for this option is 200000", i.e. one fifth of a second.
- PUBSCREEN
- PlayCD can be made to open its display on a named public screen. If the named screen does not exist, it will fall back to opening its display on the default public screen, such as the Workbench screen.
- Example:
PlayCD pubscreen=my.public.screen
- There is no default for this option. Default behaviour for PlayCD is to open its display on the default public screen which in most cases will be the Workbench screen.
- BUFMEMTYPE
- PlayCD depends upon the controller hardware the CD-ROM drive is attached to to deliver its commands properly. This may sometimes require that the command data structures are passed in a particular type of memory which the controller hardware has easy access to. In most cases you will not need to change this option, but if the CD-ROM drive is correctly configured, does support the SCSI-2 command set and still does not react to PlayCD`s commands, then it might be necessary to specify a different buffer memory type.
- Example:
PlayCD bufmemtype=2 PlayCD bufmemtype=512
- Default for this option is 0", which specifies no particular type of memory to use for interacting with the controller hardware.
The user interface
If properly configured, PlayCD will open a window which contains the following controls (left to right):
| Track display | Here you will find information about the current audio track and the playback status. The first line displays the track information, the second line indicates how much time has passed with regard to length of the current track and the entire CD. | ||||||||||
| Track position (below the track display) | This slider displays the current track position. It can also be used to change the current track position. | [Shift]+[Cursor left] and [Shift]+[Cursor right] keys | |||||||||
| Track selection | This is a set of 32 buttons, each one corresponding to one of the tracks of the audio CD. Click a button to make the corresponding audio track the current track. If playback is currently in progress, playback will proceed with the selected track. | Any number entered, e.g. entering the two digits 1 and 2 in quick succession will pick track 12. | |||||||||
| Volume | This is a vertical slider whose current setting corresponds to the sound playback volume. At the top position, playback volume is loudest. | + and - keys | |||||||||
| Eject (below the Track position slider) | Press this button to eject/load the CD in the drive. For technical reasons, you may need to press this button more than once to load a CD. | [F1] and [Backspace] keys | |||||||||
| Stop | Press this button to stop playback. | [F2] and [Cursor up] keys. | |||||||||
| Pause | Press this button to suspend/resume playback. | [F3] and [Space] keys | |||||||||
| Previous track | Press this button to skip back to the beginning of the previous track. | [F4] and [Cursor left] keys | |||||||||
| Play | Press this button to begin playback. | [F5] and [Cursor down] keys | |||||||||
| Next track | Press this button to skip forward to the beginning of the next track. | [F6] and [Cursor right] keys | |||||||||
| Shuffle | Press this button to set up a play list which contains all CD titles in random order. Playback will step through this list, playing each title once. To return to the regular play list which plays each title in the order the tracks were recorded in, press the Stop" button. | [F7] key | |||||||||
| Playback mode | This button selects a playback mode; it can be one of the following:
| ||||||||||
| Message list (below the Eject button) | This is where helpful progress reports and error messages are displayed. For example, if you picked a track by entering its number, you will see a notice confirming your input. |
Stopping the program
Once the PlayCD program is running, you can stop it by clicking on the window close gadget or by one of the keyboard equivalents [Esc] or [Ctrl]+\.
PrefsObjectsEditor
Missing description.
PrefsObjectsEditor Menus
Missing description.
PrintFiles
PrintFiles sends text files to your printer. It can accept multiple files selected with drag selection or extended selection. If PrintFiles cannot find or open one of the files, it skips it and goes to the next one. The files are printed using the settings specified in the Printer or PrinterPS Preferences editor.
To use PrintFiles:
- Select the icon of the first file to be printed, hold down Shift and select the icons of any additional files to print. You can also use drag selection to select the icons.
- Hold down Shift and double-click on the PrintFiles icon.
Tool Types
No tool types.
Shell Usage
- Format
- PRINTFILES <file> [[<file>] [<file>] ...]
- Template
- FILES/A/M
ARexx Interface
PrintFiles has no ARexx interface.
RawDisk
RawDisk reads or writes a given number of cylinders or blocks to or from a disk, transferring the data to or from a named file. The data is read or written in raw format, i.e. the disk filesystem (if any) is ignored and data is addressed absolutely.
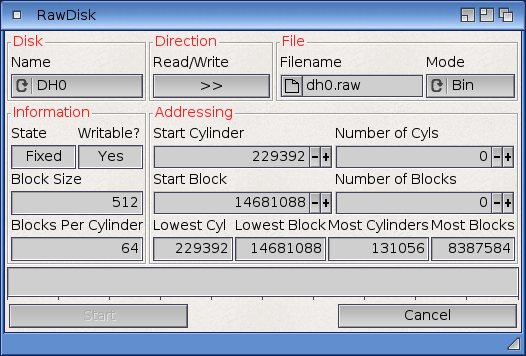
The utility can be used on any disk present in the DOS List, i.e. mounted. It can be run from Workbench by clicking the icon or from a Shell.
Disk data can be addressed by cylinders or blocks, as start + number. When reading from disk to a file, the file can be written as pure binary, hexadecimal longwords, or hexadecimal bytes. When writing from file to disk, only binary input is supported.
Tool Types
(none)
Shell Usage
- Format
- RAWDISK FROM <source> TO <target> [STARTCYLS <first cylinder>] [NUMCYLS <cylinders>]
- [STARTBLOCK <first block>] [NUMBLOCKS <blocks>] [MODE <output mode>] [QUIET]
- Template
- FROM/K/A,TO/K/A,SC=STARTCYL/N,NC=NUMCYLS/N,SB=STARTBLOCK/N,NB=NUMBLOCKS/N,MODE/K,QUIET/S
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| FROM | The source device or filename. This parameter is required. |
| TO | The destination disk or filename. This parameter os required. |
| SC or STARTCYL |
The first cylinder on the disk to be read or write. If omitted, the first cylinder on the disk will be used. If the disk has space reserved for boot blocks and filesystems, or has multiple partitions, this value might not be zero. |
| NC or NUMCYLS |
The number of cylinders to transfer. If omitted, a number of cylinders reaching from the start cylinder to the and of the disk will be assumed. If writing to disk and the input file is too small, the transfer will be zero-filled. If writing to disk and the file is too big, only part of its contents will be written to the disk. |
| SB or STARTBLOCK |
The first block to be transferred. This is simply a means of specifying a start address with smaller granularity than whole cylinders. See STARTCYL. |
| NB or NUMBLOCKS |
The number of blocks to be transferred. This is simply a means of specifying a data length with smaller granularity than whole cylinders. |
| MODE | This specifies the mode of output file (if used). The options are BIN, HEXB, and HEXL. Option BIN (binary) is the default. Option HEXB writes the data in human-readable form, as strings of hexadecimal bytes followed by the printed string (if printable). Option HEXL prints the data as strings of longwords followed by the printed string. |
| QUIET | Suppresses warning messages to Shell. |
ARexx Interface
RawDisk has no ARexx interface.
Say
With Say, Amiga can speak words typed on the screen. If the Say icon is not present, you do not have speech synthesis on your system. When you open Say, two windows appear.
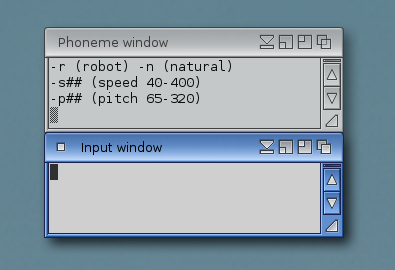
The top window is the Phoneme window, and the bottom window is the Input window. You enter text in the Input window, and the text is displayed phonetically in the Phoneme window and spoken through Amiga's audio system.
- To use Say
- 1. Select the Input window and type a word, phrase, or sentence.
- 2. After you have entered your text, press Return. Amiga will then literally say the sentence, while at the same time the text will appear in the Phoneme window. This is the phonetic interpretation of your input.
In some cases, it may help to spell a word phonetically (as it sounds) to get Amiga to repeat it correctly. You can change the voice, pitch, and speed of your Amiga's speech by choosing any of the different options shown in the Phoneme window.
- 3. Select the Input window.
- 4. Type the letter, or letters, necessary to make your changes.
- Your choices for voice and inflection are:
- -m male voice
- -f female voice
- -r robot inflection
- -n natural inflection
- When you change the voice, you can also change the pitch so the change in the new voice is noticeable.
- Type -p followed by a number from 65 through 320. The higher the number, the higher the voice's pitch. Do not put a space between the p and the number.
- To change the speed of the voice, type -s followed by a number from 40 through 400. The higher the number, the faster the voice speaks. Do not put a space between the s and the number.
- Your choices for voice and inflection are:
- 5. Press Return.
For example, to use a deep male voice with natural inflection that speaks at a moderate pace, select the Input window and type:
- -mn -s125 -p65
Then press Return. Remember that the hyphen must be typed before the alphabetical option. Next, enter some text. When you press Return, the Say program will speak your text using the new options.
To exit the Say program, select the Input window's close gadget. You can also select the Input window and press Return without entering any text. Either of these actions will close both the Input and Phoneme windows.
Tool Types
Say supports Tool Types for all the voice, pitch, and speed options. Instead of entering the options in the Input window, you can add them in the Say's Information window. This saves your selections so that they do not have to be re-entered each time you open Say. The Tool Types are:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| -m | Select a male voice |
| -f | Select a female voice |
| -r | Use robot inflection |
| -n | Use natural inflection |
| -p<pitch> | Set the pitch. A valid pitch range is between 65 and 320. The highest pitch is 320. |
| -s<speed> | Set the speed. A valid speed range is between 40 and 400. The fastest speed is 400. |
When you run Say, the options entered as Tool Types will be used, unless you specify other options in the Input window.
Shell Usage
- Format
- SAY [-m] [-f] [-r] [-n] [-s <speed>] [-p <pitch>] [-x <filename>] [<phrase>]
- Template
- [-m] [-f] [-r] [-n] [-s speed] [-p pitch] [-x filename] [phrase]
ARexx Interface
Say has no ARexx interface.
ShowConfig
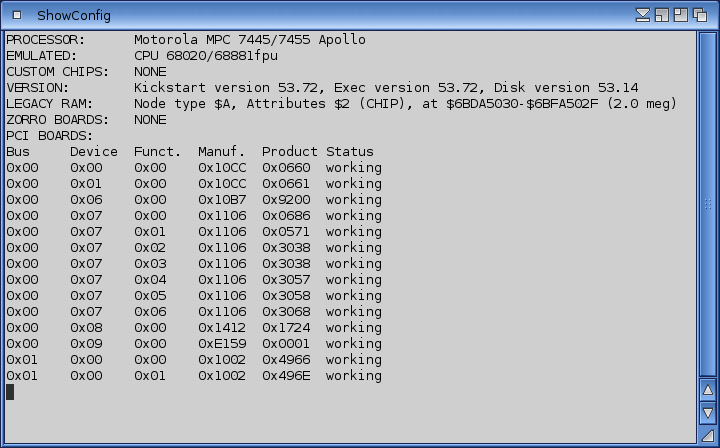
ShowConfig displays system configuration information, including processor information, custom chips, software versions, RAM information, and any plug-in boards. Double-click on the ShowConfig icon to display the information for your system. use this information when requesting hardware/software technical support.
Tool Types
ShowConfig has no Tool Types.
Shell Usage
- Format
- SHOWCONFIG [DEBUG]
- Template
- DEBUG/S
ARexx Interface
ShowConfig has no ARexx interface.
UnArc
Missing description.
UnArc Menus
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
UnArc has no ARexx interface.
USBInspector
Missing description.
USBInspector Menus
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
USBInspector has no ARexx interface.
Blankers Drawer
Missing description.
BoingBall.blanker
Missing description.
Flower.blanker
Missing description.
Forest.blanker
Missing description.
Moire.blanker
Missing description.
Pipe.blanker
Missing description.
Spiral.blanker
Missing description.
Commodities Drawer
The Commodities drawer is in the Tools drawer and contains the Commodities Exchange programs. These programs monitor your keyboard and mouse input to the Amiga.
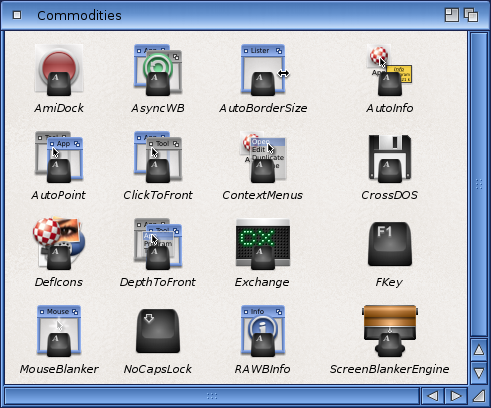
| AmiDock | A toolbar-like application launcher. |
| AsyncWB | Replaces Workbench's file execution window. |
| AutoBorderSize | Allows you to size windows at any border. |
| AutoInfo | Displays information about the icon under the pointer. |
| AutoPoint | Automatically activates the window under the pointer. |
| ClickToFront | Lets you bring a window to the front of the screen by double-clicking in it. |
| ContextMenus | Adds context menus to Workbench. |
| CrossDOS | Controls text options for CrossDOS drives. See Chapter 11 for more information. |
| DefIcons | Adds default icon functionality to Workbench. |
| DepthToFront | |
| Exchange | Monitors and controls all the other Commodities programs. |
| FKey | Assigns special functions to keys. |
| MouseBlanker | Causes the mouse pointer to go blank when you are typing. |
| NoCapsLock | Temporarily disables the Caps Lock key. |
| RAWBInfo | Replaces Workbench's icon information window. |
| ScreenBlankerEngine | Controls screen blanker. |
Using Commodities Tool Types
All of the Commodities programs share a common Tool Type:
- CX_PRIORITY=<n>
- Assigns priorities to the Commodities Exchange programs.
All the programs are set to a default priority of 0. If you enter a Tool Type that changes the priority to a higher value, that program has priority over any other Commodities Exchange program of lower priority.
For example, you can have two commodities that allow you to assign operations to functions keys. If both programs have an operation assigned to F1, the program with the higher priority intercepts the key, making it unavailable to any other Commodities programs.
There are two Tool Types that apply only to programs that open a window:
- CX_POPUP
- When set to NO, prevents the program window from opening when the icon is opened. The program activates when you double-click on its icon, but its window remains closed. The default is CX_POPUP=YES.
- CX_POPKEY
- Determines the hot key for a commodity. When the hot key or key combination is pressed, the program's window is automatically brought to the front of the screen. If the window is hidden, it is opened. Hot keys do not start commodities that are not already running. The syntax for specifying hot keys is CX_POPUP=<key>.
When specifying key combinations, leave a space between the two keys. For example:
CX_POPKEY=F9 CX_POPKEY=Shift F4 CX_POPKEY=LShift LAlt LAmiga X
Acceptable Key Combinations
When specifying key combinations for a Commodities Exchange program, you can use any of the function keys (F1 through F10) and any of the keys in the typewriter area of the keyboard (numbers, letter, symbols, and so forth). Keys from the typewriter area must be preceded by a qualifier. The allowable qualifiers are:
| Qualifier | Key |
|---|---|
| Alt | Either Alt key |
| Ralt | Right Alt only |
| LAlt | Left Alt only |
| Shift | Either Shift key |
| Rshift | Right Shift only |
| LShift | Left Shift only |
| LAmiga | Left Amiga |
| RAmiga | Right Amiga |
| CTRL | Ctrl |
| Numericpad | Specifies a key on the numeric keypad |
| Rightbutton | Hold down the menu button |
| Leftbutton | Hold down the selection button |
| Middlebutton | Hold down the middle button of a three-button mouse |
Qualifiers can also be used before function keys, but are not mandatory. You can use any combination of qualifiers; however, they must be followed by a standard key or function key. A qualifier is only recognized once in a combination:
LAlt RAmiga LAlt F10
is the same as
LAlt RAmiga F10
The following are acceptable combinations:
Alt F6 LAmiga 8 Ctrl LShift Y Leftbutton Ctrl CapsLock* Numericpad 8**
* Hold down the selection button, then press Ctrl+Caps Lock
** Use the 8 in the numeric keypad. The 8 in the normal area does not satisfy the combination.
AmiDock
Missing description.
AmiDock Menus
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
AmiDock upports the following ARexx commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ADDOBJECT FILE/A,NAME/K,ICON/K,DOCKNAME/K | This command adds a new object to an AmiDock dock. Optionally the displayed name and icon can be specified and also the name of an existant dock or subdock. The object will always be added to the main category of the given dock.
FILE specifies a path to the object which shall be added, NAME is the display name of the object, ICON is a path to the icon which shall be used for the object, and DOCKNAME tells the name of the dock to which the object shall be added. If the DOCKNAME is omitted, the object will be added to the main dock. In case of an error, variable RC is set to non-zero and variable RESULT contains the corresponding DOS error code. The FAULT command may be used to gather a descriptive error text. On success RC is set to 0. |
| ADDSUBDOCK NAME/A,ICON/K | Adds a SubDock.docky with a given name and an optional icon to the main category of the main dock. NAME is the name of the new subdock which will be displayed on the dock. ICON is a path to the icon which shall be used for the new dock.
If the command is successful, variable RC is set to 0. Otherwise RC is set to non-zero and variable RESULT contains the corresponding DOS error code. The FAULT command may be used to gather a descriptive error text. |
| FAULT NUMBER/A/N | Gives the user the text message assigned to a given error number.
On success variable RC is set to 0 and RESULT contains the requested error message. In case of an error, RC is set to non-zero and RESULT contains the following string: ERROR_OBJECT_NOT_FOUND |
| HELP COMMAND/K | Returns the command template of the named command. If the COMMAND parameter is not supplied, HELP lists all the supported commands.
On success variable RC is set to 0. In case of an error, RC is set to non-zero and variable RESULT contains the corresponding DOS error code. The FAULT command may be used to gather a descriptive error text. |
| OPEN FILE | Loads the given AmiDock XML preferences file. Beware that loading a faulty settings may lead to a bunch of error requesters of AmiDock, like not found icons. If you omit the file name, AmiDock will load its default preferences from ENVARC:.
On success command returns 0 in variable RC. In case of an error, RC is set to non-zero and variable RESULT contains the corresponding DOS error code. The FAULT command may be used to gather a descriptive error text. Note that if the user has turned on the 'autosaving' feature, the opened configuration may automatically get saved as default. Therefore it would be wise to reload the default settings at the end of your script, as long as the user did not specifically tell to save the settings as default. |
| QUIT | Tells AmiDock to quit.
Note that there is no guarantee that AmiDock will really exit after receiving the QUIT command due to a lot other things which may prevent this. Likewise AmiDock might need some time until it finally quits. So make sure you check for the (non-)existence of its ARexx port instead of simply assuming the QUIT command was successful. |
| RX CONSOLE/S,ASYNC/S,COMMAND/F | Allows the user to start an ARexx macro through the AmiDock ARexx port. The CONSOLE switch indicates that a console for a default I/O is needed, ASYNC instructs AmiDock to run the RX command asynchronously, and the COMMAND parameter should contain the macro commands to be executed.
If the command was successful, RC variable contains 0. On error RC is non-zero and the RESULT variable contains the corresponding DOS error code. The FAULT command may be used to gather a descriptive error text. |
| SAVE | Sets the current preferences as AmiDock's default preferences. |
| SAVEAS NAME/A | Saves the current preferences to a specified file. NAME should contain the name and the path where the current AmiDock configuration will be saved.
The SAVEAS command will return 0 in variable RC on success. On error RC is set to non-zero and the RESULT variable contains the corresponding DOS error code. The FAULT command may be used to gather a descriptive error text. |
AsyncWB
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
AsyncWB has no ARexx interface.
AutoBorderSize
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
AutoBorderSize has no ARexx interface.
AutoInfo
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
AutoInfo has no ARexx interface.
AutoPoint
AutoPoint lets you select windows without clocking the selection button. To start AutoPoint, double-click on ist icon. AutoPoint does not open a window.
AutoPoint automatically activates the window that is underneath the pointer, eliminating the need to click the selection button.
To disable AutoPoint, double-click on its icon a second time or open the Exchange window, select AutoPoint from the scroll gadget, and the select the Remove gadget.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
AutoPoint has no ARexx interface.
Blanker
This commodity is obsolete!
When the Blanker program is running, the screen automatically goes blank if no input has been received during a specified period of time.
The Blanker window allows you to specify the amount of time (in seconds) before the screen goes blank. The default time is 60 seconds. If you do not press a key or move the mouse during a 60 second period, the screen goes blank. To change this value, enter an alternative in the text gadget after Seconds.
Blanker can also cycle through a series of colors if you check the Cycle Colors gadget box. Checking the Animation gadget displays a random spline display.
To disable Blanker, open the Exchange window, then select Blanker, select Remove, or pick the Quit item from the Blanker window's Project menu. The hot key for Blanker is Ctrl+Alt+B.
Tool Types
Blanker has the following Tool Types:
| Tool Type | Description |
|---|---|
| SECONDS=<seconds> | The number of seconds of keyboard/mouse activity before the screen is blanked. Default is 60. |
| ANIMATION=YES|NO | Whether Blanker screen displays animation. Default is yes. |
| CYCLECOLORS=YES|NO | Whether colors on the blanker screen are cycled. Default is yes. |
ClickToFront
ClickToFront lets you bring a window to the front of the screen without selecting the window's depth gadget. To bring a window to the front with ClickToFront, hold down left Alt and double-click anywhere in the window. (The use of left Alt can be changed with Tool Types.)
To start ClickToFront, double-click on its icon. ClickToFront does not open a window.
To disable ClickToFront, open the Exchange window, select ClickToFront from the scroll gadget, then select Remove or double-click on its icon again.
Tool Types
ClickToFront supports a QUALIFIER Tool Type, allowing you to specify a qualifier key that must be pressed while double-clicking in the window you want to bring to the front of the screen. The four acceptable key arguments are:
| Lalt | Left Alt (Default) |
| Left_Alt | Left Alt |
| Ralt | Right Alt |
| Right_Alt | Right Alt |
| CTRL | Ctrl |
| CONTROL | Ctrl |
| None | No qualifier necessary |
For example, if you have specified QUALIFIER=CTRL and ClickToFront is activated, hold down Crtl and double-click in the window you want frontmost.
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
ClickToFront has no ARexx interface.
ContextMenus
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
ContextMenus has no ARexx interface.
CrossDOS
The CrossDOS commodity controls text options for active CrossDOS drives. The CrossDOS commodity window shows the available drives and allows you to set Text Filtering or Text Translation separately for each Hot key: Ctrl+Alt+C. For more information on the CrossDOS commodity, see Chapter 11.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
CrossDOS has no ARexx interface.
DefIcons
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
DefIcons has no ARexx interface.
DepthToFront
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
DepthToFront has no ARexx interface.
Exchange
Exchange manages the background utilities contained in the Commodities drawer. The hot key for Exchange is Ctrl+Alt+Help.
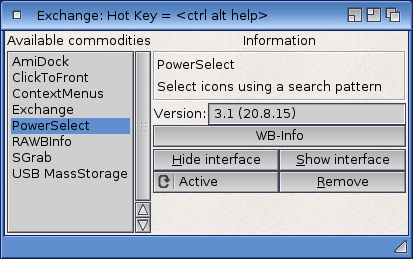
The Exchange window lists the commodities that are running and displays information about each one as it is selected.
| Remove | Turns off commodities. |
| Show Interface | Displays the commodity window, allowing you to interact with it as if you pressed the commodity's hot key. |
| Hide Interface | Closes the commodity window without turning the commodity off. |
Exchange Menus
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
Exchange has no ARexx interface.
FKey
FKey allows you to assign functions to keys, eliminating the need for repetitive typing.
When you double-click on the FKey icon, the following window appears:
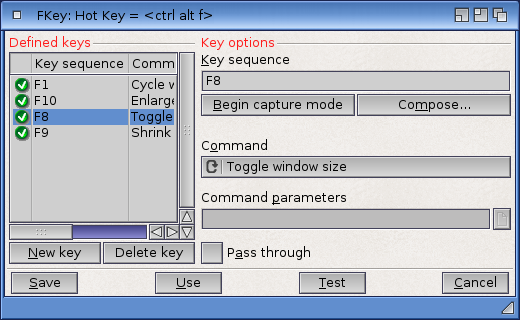
FKey lets you assign any of eight commands to any key sequence that you can enter.
The Defined Keys scrolling list shows all the currently defined key sequences.
The New Key and Delete Key gadgets let you add and remove key sequences.
The Command cycle gadget lets you pick a command for the current key sequence. The possible commands are:
| Cycle Windows | Brings the rearmost application window on the Workbench screen to the front of the display and selects it. |
| Cycle Screens | Brings the rearmost screen to the front of the display. |
| Enlarge Window | Enlarges the selected window to its maximum size, taking into account the edges of the screen. |
| Shrink Window | Shrinks the selected window to its minimum size. |
| Toggle Window Size | Zooms the selected window as if you had selected its zoom gadget. It also works on windows that only have a zoom gadget and no sizing gadgets. |
| Insert Text | When the key sequence is entered, the specified string is inserted in a console window or text gadget. It has no effect if something that accepts keyboard input is not selected. The string to insert is specified in the Command Parameters gadget. |
| Run Program | Lets you run a program by entering any key sequence. The program name and its arguments are specified in the Command Parameters gadget. |
| Run ARexx Script | Lets you run an ARexx script by entering any key sequence. The script name and its arguments are specified in the Command Parameters gadget. Putting quotes around the script name turns it into an ARexx string file. |
The Command Parameters text gadget lets you specify arguments for three of the commands.
For example, to designate Alt F1 as the key sequence to start MultiView, follow these steps:
- Select the New Key gadget.
- Enter the key sequence in the string gadget as Alt F1 (be sure to enter a space between Alt and F1).
- Select the Run Program option in the Command cycle gadget.
- Enter the path for MultiView (SYS:Utilities/MultiView) in the Command Parameters text gadget.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
FKey has no ARexx interface.
MouseBlanker
MouseBlanker blanks the mouse pointer from the display when you are typing at the keyboard. The mouse pointer returns to the screen when you move the mouse again.
To enable MouseBlanker, double-click on its icon. To disable MouseBlanker, double-click on its icon again or open the Exchange window, select MouseBlanker from the scroll gadget, and select the Remove gadget.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
MouseBlanker has no ARexx interface.
NoCapsLock
NoCapsLock disables the Caps Lock key. The Shift keys still function normally, but Chaps Lock has no effect if pressed accidentally.
To start NoCapsLock, double-click on its icon. It does not open a window. To disable NoCapsLock, open the Exchange window, select NoCapsLock from the scroll gadget, and select the Remove gadget or double-click on its icon again.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
NoCapsLock has no ARexx interface.
RAWBInfo
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
RAWBInfo has no ARexx interface.
ScreenBlankerEngine
Missing description.
Tool Types
Shell Usage
- Format
- Template
ARexx Interface
ScreenBlankerEngine has no ARexx interface.
Dockies Drawer
Missing description.
Access.docky
Missing description.
Anim.docky
Missing description.
Button.docky
Missing description.
Clock.docky
Missing description.
Debugger.docky
Missing description.
Fancy.docky
Missing description.
Lens.docky
Missing description.
Minimizer.docky
Missing description.
Online.docky
Missing description.
Rainbow.docky
Missing description.
Separator.docky
Missing description.
Spacer.docky
Missing description.
SubDock.docky
Missing description.
Test.docky
Missing description.