Copyright (c) Hyperion Entertainment and contributors.
AmigaDOS Vector-Port
Rationale
During development of file systems, the developer often needs to write a lot of code just to interface with DOS library. The new Vector-port interface simplifies this by delegating most of this interface work to the DOS Library. This means that the developer writing the file system can concentrate on implementing the functions required.
Introduction
In the past, DOS library used to communicate with file systems and handlers using DOS packets exclusively. A DOS packet is merely an Exec Message with parameters and results appended. The aim of this format is to remain as generic as possible with abstracted parameters. Unfortunately, this approach requires more overhead work for the developer to handle the packet, extract arguments from it and return results to it.
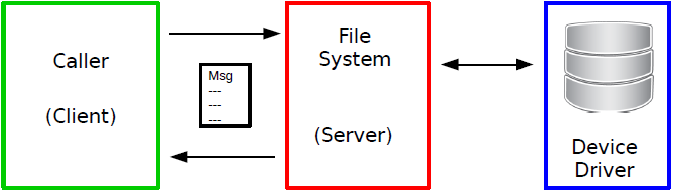
DOS packet-based file systems:
- The server is asynchronous with the client.
- Client can perform other tasks while waiting for the server.
- Task switching is relatively slow.
- Server must have access to client's address space.
Examples of DOS pack-based file systems include:
- OFS (Old File System)
- FFS, FFS2 (Fast File System)
- SFS, SFS2, JXFS (Smart File System)
- PFS3 (Professional File System)
Starting with version 53.77, DOS Library offers the new Vector-Port API, exclusively for file systems. It is basically a Message port with an associated function list (also called 'table of vectors' thus the API name). In this way, we are freed from many legacy constructs (notably BPTRs and BSTRs) and the arguments are clearly defined. The semantics of each function are now defined, so different file systems should behave identically when written to follow the API rules.
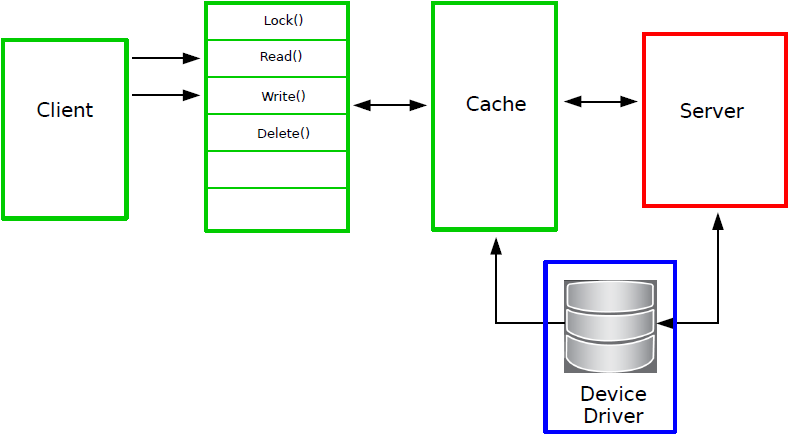
DOS vector-port-based file systems:
- Remove the need for task switching.
- Server has access to client's address space.
- Specific syntax and semantics of API to prevent variations.
- Eliminates overlap of responsibilities between DOS and server.
- Eliminates duplication of code in file systems and DOS.
Examples of DOS vector-port-based file systems include:
- NGFS (Next Generation File System)
- ENV: (env-handler)
- RAM: (ram-handler)
| Times Have Changed |
|---|
| In the 68K days, I/O speed took the vast majority of time when compared to the Task switching speed. Today, I/O speed has increased to the point where Task switching speed is now taking the majority of the time. |
Legacy Support
Since version 53.95, DOS Library provides DOS packet emulation for legacy applications that still send DOS packets directly to the file system's Message Port. This allows these old applications to work seamlessly with a complete Vector-Port based file system. This special DOS packet emulation functionality converts these 'application-sent' DOS packets to equivalent Vector-Port calls.
Existing file system conversion
DOS allows for a step by step conversion of existing file systems to the Vector-Port API by falling back to sending a DOS packet when any Vector-Port function is NULL or the Vector-Port itself does not validate. This means that one can convert single functions one at a time by simply adding or removing the function vector from the Vector-Port initialisation table.
Key points
Formerly a file system was required to allocate a Message Port. Now it only needs to replace this creation by a call to DOS method AllocDosObject(), requesting creation of a Vector-Port and providing it the list of implemented functions. Everything else is automatically handled. If unimplemented functions are called, DOS library falls back to sending a DOS packet. The advantage of this solution is that it uses direct function calls, so is substantially faster than sending a message and waiting for its handling by the file system. It is also processed on the caller's context thus we benefit from the OS multitasking feature to parallelize calls and there is no expensive context switching.
Examples
The new vector-port API is already used by ram-handler and env-handler.
Example for ACTION_LOCATE_OBJECT DOS packet and the corresponding "Vector-Port" function FSLock():
INPUTS (DosPacket method)
dp_Type - (int32) ACTION_LOCATE_OBJECT
dp_Arg1 - (BPTR) rel - Name reference lock.
dp_Arg2 - (BSTR) name - Object name. (may also include path)
dp_Arg3 - (int32) mode - SHARED_LOCK or EXCLUSIVE_LOCK.
dp_Arg4 - <unused> 0
dp_Arg5 - (BSTR) nameformat - name format indicator value.
only if(dp_Arg2==dp_Arg5) then BSTR's are guaranteed
to be nul-terminated. (53.23)
RESULT1 - (BPTR) Lock - (ZERO on failure.)
RESULT2 - (int32) Failure code if RESULT1 == ZERO
INPUTS (FileSystemVectorPort method)
struct Lock * RESULT1 = FSLock(struct FileSystemVectorPort *fsvp,
int32 *result2, struct Lock *rel,
CONST_STRPTR name, int32 mode);
fsvp - (struct FileSystemVectorPort *) Pointer to the vector port.
result2 - (int32 *) Pointer to the storage area for RESULT2.
rel - (struct Lock *) Pointer to the 'name' reference lock.
name - (CONST_STRPTR) Pointer to the object name.(no path component)
mode - (int32) SHARED_LOCK or EXCLUSIVE_LOCK.
RESULT1 - (struct Lock *) Pointer to the lock, NULL on failure.
RESULT2 - (int32) Failure code if RESULT1 == NULL
Developer tools
FSVPtool creates a ready to use skeleton to help with creation of new file systems. This tool is available in the latest SDK.
FSTest is a tool to test your file system for compliance. Even the most mature file systems are not 100% compliant as this tool will demonstrate.
Disk I/O Library
More assistance to the file system developer is available via the DiskIO Library.
More information
For further details and example code, refer to the autodoc: dos.dospackets.doc