Copyright (c) Hyperion Entertainment and contributors.
AmigaOS Manual: Workbench Using: Difference between revisions
Steven Solie (talk | contribs) |
Steven Solie (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
| Tools || Is available for applications to use or for user-created menu items. |
| Tools || Is available for applications to use or for user-created menu items. |
||
|} |
|} |
||
=== Workbench Menu === |
|||
The Workbench menu contains general Workbench options and options for windows opened on the Workbench screen. You can, for example, use the Workbench menu to update the screen display or see which version of the system software is in use. |
|||
On the Workbench menu you can select the following options: |
|||
==== Backdrop ==== |
|||
The Backdrop menu item creates more room on the Workbench screen for displaying windows and icons. Backdrop switches between a normal window for your Workbench and a special borderless window that is always behind other windows opened on the Workbench. |
|||
Choosing Backdrop removes the Workbench window borders so that the disk icons appear to be on the Workbench screen without being enclosed in a window. To return to the normal Workbench window, choose Backdrop again. Backdrop is reset to off if you power off or reboot your computer. To save your Backdrop selection choose the Snapshot item in the Windows menu while the Workbench window is selected. |
|||
==== Execute Command ==== |
|||
{{Note|This menu item is provided for users familiar with AmigaDOS.}} |
|||
The Execute Command executes (starts) an AmigaDOS command without opening a Shell window. Figure 4-2 illustrates an Execute Command requester. |
|||
[[File:WorkbenchFig4-2.png|frame|center|Execute Command Window]] |
|||
Enter the command and all of its arguments in the requester. |
|||
A Workbench Output Window is automatically opened when a command results in output and it remains there until you select its close gadget. The current directory for an Execute Command operation is RAM:. |
|||
Revision as of 22:25, 3 February 2014
This chapter describes the Amiga Workbench, an icon-based environment that allows you to give instructions by manipulating graphic symbols with a mouse rather than by typing in commands at a keyboard. Included in this chapter are descriptions of the following:
- The Workbench Screen
- The Workbench Window
- The Workbench Menus
- Workbench Programs
Workbench Screen
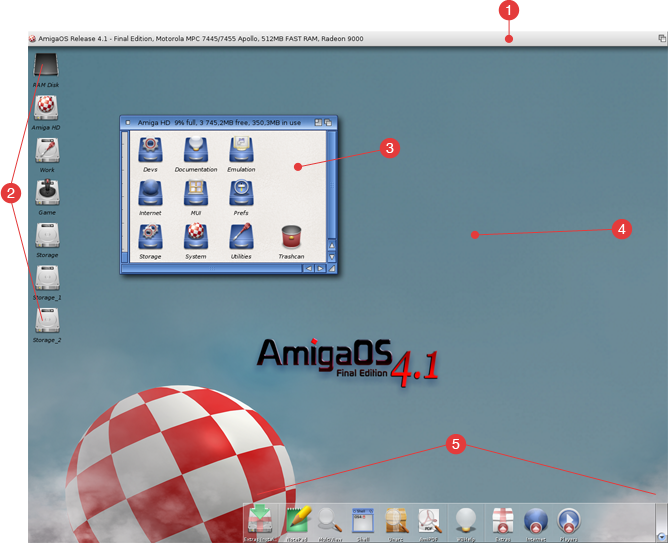
The Workbench screen, illustrated in Figure 4-1, is the primary visual component of your system. Icons and other windows appear on it.
The Workbench screen is identified by the Amiga Workbench title bar located along the top border of the display. The Workbench screen's title bar also displays the number of bytes of graphics (Chip) memory and other (Fast) memory currently available when any window, except a Shell window is selected.
The Amiga provides Preferences editors (described in Chapter 5) that allow you to customize the Workbench screen. You can define an extra-large virtual Workbench screen that is larger than the viewable area with more space for windows.
Workbench Window
When you boot you Amiga, the Workbench window fills the Workbench screen. This window contains icons for any floppy disks inserted into floppy drives, the Ram Disk, and any other icons determined by your system's configuration.
Although the Workbench window appears and functions like an application window, it is an essential part of the Workbench screen.
Workbench Menus
The workbench has the following four menus:
| Workbench | Contains options for working with Workbench and windows opened on the Workbench screen. |
| Windows | Contains options for working within the currently selected window. |
| Icons | Contains options for working with the currently selected icon or group of icons. |
| Tools | Is available for applications to use or for user-created menu items. |
Workbench Menu
The Workbench menu contains general Workbench options and options for windows opened on the Workbench screen. You can, for example, use the Workbench menu to update the screen display or see which version of the system software is in use.
On the Workbench menu you can select the following options:
Backdrop
The Backdrop menu item creates more room on the Workbench screen for displaying windows and icons. Backdrop switches between a normal window for your Workbench and a special borderless window that is always behind other windows opened on the Workbench.
Choosing Backdrop removes the Workbench window borders so that the disk icons appear to be on the Workbench screen without being enclosed in a window. To return to the normal Workbench window, choose Backdrop again. Backdrop is reset to off if you power off or reboot your computer. To save your Backdrop selection choose the Snapshot item in the Windows menu while the Workbench window is selected.
Execute Command
| Note |
|---|
| This menu item is provided for users familiar with AmigaDOS. |
The Execute Command executes (starts) an AmigaDOS command without opening a Shell window. Figure 4-2 illustrates an Execute Command requester.
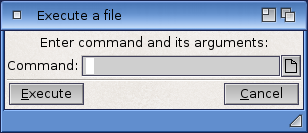
Enter the command and all of its arguments in the requester.
A Workbench Output Window is automatically opened when a command results in output and it remains there until you select its close gadget. The current directory for an Execute Command operation is RAM:.