Copyright (c) Hyperion Entertainment and contributors.
AmigaOS Manual: Workbench Using
This chapter describes the Amiga Workbench, an icon-based environment that allows you to give instructions by manipulating graphic symbols with a mouse rather than by typing in commands at a keyboard. Included in this chapter are descriptions of the following:
- The Workbench Screen
- The Workbench Window
- The Workbench Menus
- Workbench Programs
Contents
- 1 Workbench Screen
- 2 Workbench Menus
- 3 Workbench Programs
- 3.1 System Drawer
- 3.2 Utilities Drawer
- 3.2.1 AmiGS
- 3.2.2 AmiPDF
- 3.2.3 Calculator
- 3.2.4 Clock
- 3.2.5 More
- 3.2.6 GraphicDump
- 3.2.7 IconEdit
- 3.2.8 InitPrinter
- 3.2.9 Installation Utility
- 3.2.10 KeyShow
- 3.2.11 MEmacs
- 3.2.12 MultiView
- 3.2.13 NotePad
- 3.2.14 PartitionWizard
- 3.2.15 PlayCD
- 3.2.16 PrefsObjectsEditor
- 3.2.17 PrintFiles
- 3.2.18 RawDisk
- 3.2.19 ShowConfig
- 3.2.20 UnArc
- 3.2.21 USBInspector
- 3.3 Internet Drawer
- 3.4 Emulation Drawer
- 3.5 WBStartup Drawer
- 3.6 Expansion Drawer
- 3.7 Devs Drawer/Storage Drawer
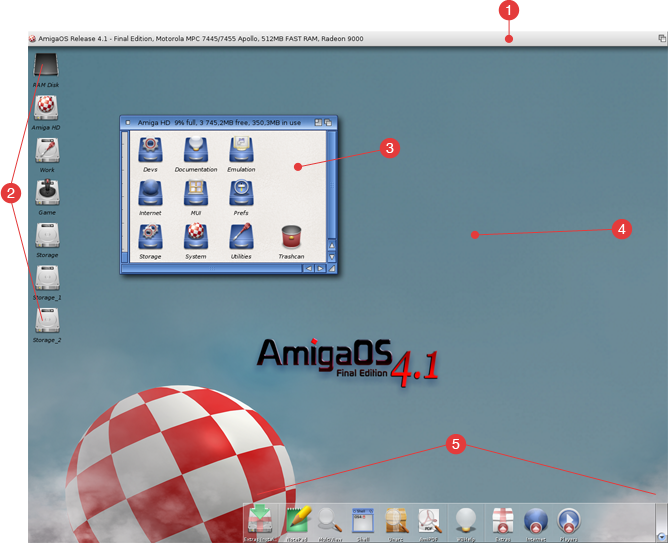
Workbench Screen
The Workbench screen, illustrated in Figure 4-1, is the primary visual component of your system. Icons and other windows appear on it.
The Workbench screen is identified by the Amiga Workbench title bar located along the top border of the display. The Workbench screen's title bar also displays the number of bytes of graphics (Chip) memory and other (Fast) memory currently available when any window, except a Shell window is selected.
The Amiga provides Preferences editors (described in Chapter 5) that allow you to customize the Workbench screen. You can define an extra-large virtual Workbench screen that is larger than the viewable area with more space for windows.
Workbench Window
When you boot you Amiga, the Workbench window fills the Workbench screen. This window contains icons for any floppy disks inserted into floppy drives, the Ram Disk, and any other icons determined by your system's configuration.
Although the Workbench window appears and functions like an application window, it is an essential part of the Workbench screen.
Workbench Menus
The workbench has the following four menus:
| Workbench | Contains options for working with Workbench and windows opened on the Workbench screen. |
| Windows | Contains options for working within the currently selected window. |
| Icons | Contains options for working with the currently selected icon or group of icons. |
| Tools | Is available for applications to use or for user-created menu items. |
Workbench Menu
The Workbench menu contains general Workbench options and options for windows opened on the Workbench screen. You can, for example, use the Workbench menu to update the screen display or see which version of the system software is in use.
On the Workbench menu you can select the following options:
Update software
Backdrop
The Backdrop menu item creates more room on the Workbench screen for displaying windows and icons. Backdrop switches between a normal window for your Workbench and a special borderless window that is always behind other windows opened on the Workbench.
Choosing Backdrop removes the Workbench window borders so that the disk icons appear to be on the Workbench screen without being enclosed in a window. To return to the normal Workbench window, choose Backdrop again. Backdrop is reset to off if you power off or reboot your computer. To save your Backdrop selection choose the Snapshot item in the Windows menu while the Workbench window is selected.
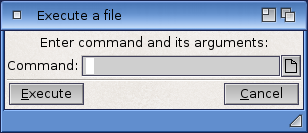
Execute Command
| Note |
|---|
| This menu item is provided for users familiar with AmigaDOS. |
The Execute Command executes (starts) an AmigaDOS command without opening a Shell window. Figure 4-2 illustrates an Execute Command requester.
Enter the command and all of its arguments in the requester.
A Workbench Output Window is automatically opened when a command results in output and it remains there until you select its close gadget. The current directory for an Execute Command operation is RAM:.
Open volume
Redraw All
Redraw All redraws all open Workbench windows in the Workbench screen and can be used in the event of a disturbance to the Workbench. If Redraw All does not restore the windows to their proper appearance, reboot the computer.
Update All
Update All reopens each open Workbench window, updating its appearance to show its current state.
| Note |
|---|
| If you have several windows open and have been using the Shell or an application to change to the contents of a disk, the changes may not be reflected in its windows until you close the windows and reopen them or choose Update All. |
Last Message
Last Message retrieves the last information or error message that appeared on the title bar.
About
About opens a requester showing the internal version number of the Workbench and Kickstart software, as well as copyright information. Select the OK gadget to close the requester.
Quit
Quit closes all Workbench operations, making additional RAM available if needed. The Workbench does not close if there are any programs running, including programs that do not open a window and programs that are in your WBStartup drawer.
The only windows that can remain open while using Quit are the disk, drawer, and Shell windows. Once you OK the Quit requester, a Shell window is your only link to the Amiga. You can use the Shell icon in the System drawer to open a Shell window before quitting the Workbench.
Return to the Workbench by typing LOADWB (load Workbench) at the Shell prompt and pressing Return. If there is no Shell window open, you must reboot to return to the Workbench.
The close gadget on the Workbench window is the same as choosing Quit.
Window Menu
The Window menu is only available when a Workbench window is selected. The Window menu allows you to create new drawers, select the contents of the window, rearrange the contents, change how the contents are displayed, and close the window. The available window options are:
New Drawer
To create a new drawer:
- Select the window in which you want to create the drawer.
- Choose New Drawer from the Window menu. The drawer is created and named "Unnamed1".
- A Rename requester prompts you to change the name of the drawer.
- Delete the existing name using the DEL key, enter a new name, and press Return or select OK. Selecting Cancel leaves the default name on the new drawer.
Open Parent
A window's parent is the window that contains its icon. With the exception of the Workbench window, every Workbench disk window has a parent window.
Open Parent opens the selected window's parent or brings it to the front of the display if it is already open.
Close
Close closes and removes the selected window from the screen.
Mouse shortcut: For many windows, you can select the close gadget in the upper left corner of the window.
Update
Update redraws the selected window, including any changes made to the contents through the Shell or the Execute Command menu item. Such changes are not reflected until the window is updated or reopened.
Select Contents
Select Contents selects all of the icons in the current window.
Clean Up
Clean Up automatically arranges all the icons in the selected window so that they do not overlap. This arrangement is not saved until you use the Snapshot menu item described below.
Snapshot
Snapshot saves the arrangement and position of icons in a window. It is commonly used following Clean Up. Snapshot has a submenu containing two items: Window and All.
Snapshot Window saves the position and size of the selected window, as well as the Show and View By settings described below. However, it does not save the position of the icons in the window.
Snapshot All saves the position and other settings of all the icons in the selected window, as well as the position and size of the window.
Show
Show controls the types of icons that are displayed on a window. Show has two submenu items: Only Icons and All Files.
Show Only Icons is the default Show mode, displaying only those files and drawers that have icons (.info files).
Show All Files provides a pseudo-icon for each file or drawer in the selected window that does not have a real icon. Pseudo-icons can be treated like any other icon, including manipulating them with the menu items in the Icon menu.
You may have to scroll in the window to see the new pseudo-icons.
View By
View By changes how the information in the window is displayed. View By has four submenu items: Icons, Name, Date, and Size.
View By Icons is the window's default mode.
Choosing View By Name, View By Date, or View By Size displays a window's contents in text form, including the size of the file, its attributes (whether it can be read, deleted, executed, or written to), and its timestamp.
File and drawer names can be selected, opened, dragged, and manipulated just like icons.
View By Name sorts the file list in alphabetical order.
View By Date sorts the list in chronological order, with the most recently created file listed first.
View By Size sorts the list by size, listing the smallest file first.
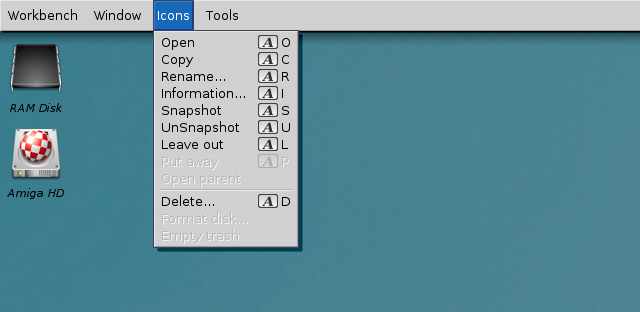
Icons Menu
The Icons menu allows you to work with the icons on the screen. An icon must be selected before the menu options illustrated in Figure 4-3 become available.
Open
Opening an icon makes a program or window available.
When you open a disk or drawer icon, a window displays the icons contained on that disk or in that drawer. When an individual project or tool is opened, the corresponding program starts.
Open an icon by selecting it an choosing Open.
Mouse Shortcut: Point to the icon and double-click the selection button.
Copy
Copy allows you to duplicate disks, drawers, programs, or files within a window. To copy material to another window, use the drag-copy method described in Chapter 3. Drag-copying is the easiest method of copying a disk on a two-floppy-system.
Use Copy for making backup copies of your disks.
To copy a drawer, project, or icon:
- Select the icon.
- Choose Copy from the Icons menu.
Copying disks on single-floppy disk drive systems entails a process known as swapping. Source and destination disks are swapped in the single drive as the system first reads information from the source disk and the writes it to the destination disk. The destination disk must be write-enabled, but need not be formatted since Copy formats the disk as it writes to it. Be sure to copy to disks of the same density as the original disks.
To copy a disk on a single-floppy disk drive system:
- Insert the source disk into the Amiga's internal disk drive.
- Select the source disk's icon.
- Choose Copy from the Icons menu. Insert the Workbench disk, if necessary.
- If the disk copy requires at least five swaps, a requester tells you how many swaps are needed. Closing any unnecessary windows or stopping any unwanted programs helps reduce the number of swaps.
- Select the Continue gadget in the swap requester. During the disk copy, the icon for the disk being copied is unavailable and is labeled "BUSY".
- Insert the source disk into the drive when prompted and select Continue. A horizontal bar gauge shows the percentage of the disk copy completed.
- Insert the destination disk into the drive when prompted and select Continue to copy the information read in from the source disk. Swap the disks as often as requested. When the copy is finished, a Disk Copy Finished message appears.
- Remove the destination disk from the drive and label it. The destination disk's icon is labeled with a copy_of_prefix (for example, copy_of_DataDisk).
Rename
Rename changes the name of an icon. It is used to remove the copy_of_prefix from something you copied, as well as for changing the names of drawers, disks, and files.
To rename an icon:
- Select the icon.
- Choose Rename from the Icons menu. A requester containing a text gadget displays the current name of the icon.
- Delete the old name using Backspace or right Amiga+X and enter the new name. Do not use spaces before or after the new name. Because embedded spaces are not visible, they can cause confusion if you have to type in the icon name again.
- Press Return. The new name appears under the icon.
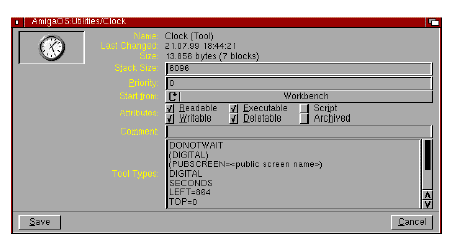
Information
Information displays status information about the selected icon's file. Certain data can also be modified in the Information window. Figure 4-4 illustrates the Information window.
Although the contents of the window varies with the icon, the following information is always displayed:
| title bar | The window title bar indicates the path to the icon. |
| name | The icon name and its type in parentheses (Volume, Drawer, Tool, Project, or Trashcan). |
| image | A picture of the icon. |
| size | The number of blocks and bytes that the disk, project, or tool fills. |
| stack | The amount of memory reserved as temporary storage for a specific tool. |
| last changed date | The date on which the icon was created or the last time it was changed (its timestamp). |
For a disk icon, the window also shows whether a disk is write-enabled (Read/Write) or write-protected (Read Only).
For a drawer, trashcan, project, or tool, the following attributes can be set or cleared by clicking on the attribute's check box.
| Script | If set, the file is a script (a text file of AmigaDOS commands) and can be run without using the EXECUTE command. |
| Archived | This attribute is set by backup programs to indicate that a file or directory has been archived (backed up). It is cleared whenever the file is saved. |
| Readable | If set, information in the file can be read. If this attribute is clear, a tool will not run and a project cannot be loaded by its Default Tool. |
| Writable | If set, information can be written into the file. Unless Writable is set, you cannot make changes to the file. |
| Executable | If set, the file is a tool that can be run from Workbench or the Shell. If this attribute is clear, the tool cannot be run from the Shell. |
| Deletable | If set, the drawer, project, or tool can be erased from the disk. If clear, the object is protected from deletion. |
If the icon represents a project, there is a Default Tool gadget. This specifies the path to the tool that created the project. When the project icon is opened, the default toll is also opened to work on the project.
If there is a Comments box, you can add a note of up to 79 characters by selecting the text gadget next to Comments, entering the text, and pressing Return.
The Tool Types box specifies different startup options for some programs or files. Icon Tool Types are described in Chapter 3.
To save any changes made to the Information window, select the Save gadget in the lower left corner.
Snapshot
Snapshot saves the positions of all the currently selected icons. The next time you open the window, the icons that you selected appear in their saved positions. You can save the positions of several icons at one time by using drag selection or extended selection.
To save the position of an icon:
- Select the icon.
- Choose Snapshot.
UnSnapshot
UnSnapshot cancels the snapshot position of an icon. The next time you open the window, the icons are rearranged.
To release the snapshot position of an icon:
- Select the icon.
- Choose UnSnapshot.
Leave Out
Leave Out moves an often-used icon out of its original window and into the Workbench window for faster access. The file represented by the icon remains in its original drawer on the disk; only the icon is moved. The icon remains in the Workbench window, even if the machine is rebooted. This menu item cannot be used with disks or the Trashcan.
To use Leave Out:
- Select the icon.
- Choose Leave Out.
The icon moves into the Workbench window.
Put Away
Put Away returns an icon that was left out to its original drawer.
To use Put Away:
- Select the icon.
- Choose Put Away.
Delete
Delete erases files and their icons from your disks.
| Caution |
|---|
| Use Delete with caution; you cannot retrieve something that was deleted. |
To delete a file or drawer:
- Select its icon. Use drag selection or extended selection to choose more than one icon to be deleted. Disks and the Trashcan cannot be removed with Delete.
- Choose Delete from the Icons menu. A warning requester appears, listing the number of files and drawers currently selected. Verify that you want to erase permanently the items listed. Remember that if you delete a drawer, everything contained in it is also deleted.
- Select the OK gadget. The icon and the files associated with it are erased from your disk. If you do not want to delete everything currently selected, select the Cancel gadget.
Format Disk
Formatting a disk prepares it for storing information. Format disks that are new and unformatted, disks that develop errors, or disks on which you wish to use different file system options.
| Caution |
|---|
| Formatting erases all information on a disk. Be careful not to format disks that hold information that you do not want to lose, particularly your original system and software applications disks. |
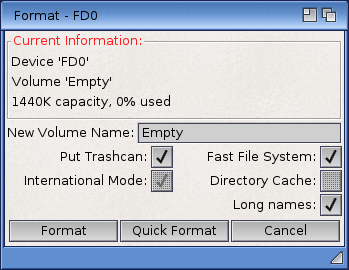
Select the icon of the disk to be formatted and choose Format Disk from the Icons menu. The Format window, illustrated in Figure 4-5, displays the current information about the disk. If the disk is already formatted, its volume name and the percentage of the disk currently in use are displayed. A text gadget allows you to enter a new Volume name for the disk.
Four items can be selected (checked) in the Format window:
| Put Trashcan | Allows you to put a Trashcan on the disk. |
| Fast File System | Allows the Amiga to fit more information on a disk. It is faster than the standard file system. Fast File System disks are incompatible with Workbench software releases prior to Release 2. |
| International Mode | Fully supports international characters in file names. We recommend that you set this option on. International Mode is incompatible with Workbench software releases prior to Release 2. |
| Directory Cache | Speeds up the opening of drawers, file requesters, and listings. This option is off by default. Disks using Directory Cache are incompatible with Workbench software releases prior to Release 3. |
Fast File System, International Mode, and Directory Cache can only be specified for AmigaDOS disks. Selecting the Directory Cache option automatically selects International Mode. Disks created with the Directory Cache option can only be read by Amigas running Workbench Release 3.0 and above.
Quick format is for reformatting a disk that was previously formatted. You cannot format a new blank disk with Quick Format. Choosing the Quick Format option is faster than formatting the entire disk; however, it does not detect any read/write errors on the disk that could be eliminated by a full format.
When the disk is formatted, if you did not change he name in the Format window, it is labeled Empty. This name can be changed using the Rename item in the Icons menu.
Formatting Hard Disks
You must format your hard disk under the following conditions if:
- It is a new unformatted disk.
- You have a serious unrecoverable disk error.
- You have repartitioned the disk.
- You wish to use a different file system option on the disk, such as the Directory Cache option.
Before reformatting your hard disk, be sure to back up all important information from the disk.
The Ram Disk cannot be formatted. If you accidentally select the Ram Disk for formatting, a requester reports that there is a format failure and requires you to select Cancel.
If you have more than one disk icon selected, more than one Format window opens when the Format Disk item is selected from the Icons menu. The format windows open one on top of another so that only one Format window is initially visible. Drag the windows until all are visible. Be sure to check the Current Information field in the Format window for the intended Device and Volume names before allowing the format to continue.
| Caution |
|---|
| Check the device and volume names carefully. If you accidentally reformat your hard disk instead of a floppy, you will eras all of your files. |
Formatting Floppy Disks
The Amiga does not recognize floppy disks that are not formatted; therefore, blank disks must be formatted before anything can be written on them. Disks can be formatted at any time, including while running one or more applications. Disks usually have to be formatted only once.
To determine if a floppy disk is formatted, insert it into a floppy drive and check the disk icon on the Workbench screen. If the Amiga cannot recognize the disk, four question marks (????) follow the drive designation in the icon's label.
To format a blank disk:
- Write-enable the disk and insert it into a floppy drive.
- Select its disk icon when it appears on the Workbench screen.
- Holding down the menu button, point to the Icons menu, move the pointer to the Format Disk item, and release the button.
- If you have a hard drive on your Amiga, skip to Step 7. If you do not have a hard drive on your Amiga, at the requester insert the workbench disk into any drive.
- When the Format program has been loaded from the Workbench disk remove the disk from the drive.
- At the requester, insert the blank disk and select the Continue gadget.
- In the Format window, change the volume name of the disk from the default Empty; choose whether to put the Trashcan on the disk an other options. Then select Format to continue.
- A requester warning that all data will be lost if you continue the format appears on the screen. Select either Format or Cancel.
- During the format a window is displayed that shows the percentage of disk that has been formatted. This window also has a Stop gadget that allows you to cancel the format at any time.
A disk that is partially formatted is not usable.
To format a disk as an MS-DOS disk through CrossDOS, you must have a CrossDos DOSdriver activated. If the PC0 DOSdriver is active, select the disk icon labeled PC0:???? for formatting.
Empty Trash
Empty Trash deletes the contents of the Trashcan. To use the Trashcan, drag an icon over the Trashcan icon and release the selection button. The icon is then stored in the Trashcan drawer until you decide to permanently throw it away with Empty Trash.
To delete an icon with Empty Trash:
- Drag the icon over the Trashcan and release the selection button. If you open the Trashcan, the icon appears in the Trashcan window.
- Make sure the Trashcan icon is selected (the lid is displayed open) and choose Empty Trash from the Icons menu. The Trashcan contents are deleted.
An icon can be retrieved from the Trashcan as long as Empty Trash is not chosen. Retrieve an icon by opening the Trashcan window and dragging the icon into any window. You may wish to open the Trashcan window in Show All Files mode and verify its contents before choosing Empty Trash.
The following rules apply to the Trashcan:
- Icons can only be moved to a Trashcan on the same volume.
- Disks cannot be deleted using the Trashcan.
- The Trashcan cannot be moved into a drawer.
- The Trashcan cannot be left out.
- The Trashcan cannot be deleted with the Delete menu item.
Tools Menu
The Tools Menu initially contains only ResetWB for resetting the Workbench. Other Amiga applications and utilities can add items to the Tools menu. Consult the documentation that came with your applications software for information on adding items to the Tools menu.
Workbench Programs
The Workbench disk window contains a number of drawers that contain system and utility files.
These drawers are:
- System
- Utilities
- Devs
- Storage
- WBStartup
- Expansion
System Drawer
The System drawer contains programs that control system functions. Some offer access to Amiga accessory programs, such as AmigaDOS or ARexx.
Find
Find allows you to search files by name or by contents.
FixFonts
FixFonts should be used after fonts are added to or deleted from your Fonts drawer.
For more information on fonts and FixFonts, see Chapter 8.
Format
Format a disk by opening the Format icon. Double-clicking on the Format icon opens a requester asking you to select a device to format. Click on the device you wish to format. Click on the Continue button to display the Format window. The rest of the procedure follows the same steps as used with t he Icon menu's Format Disk item, described on page 4-17.
FormatCDRW
FormatCDRW allows you to format a rewriteable optical disk.
GrimReaper
GrimReaper is a system tool for handling software failures. It is launched automatically when software failure occurs.
Help
Help allows you to read Shell command documentation.
Intellifont
Intellifont manages the installation of Intellifont® outline fonts onto your Amiga. Intellifont and fonts are described in Chapter 8.
Media Toolbox
Disk partition tool.
Mounter
Mounter is an interactive partition mount tool. It operates on devices that support the RDB (Rigid Disk Block) organization data structures which define which and which size partitions are assigned to a storage medium.
NoFastMem
Some very old programs may not run properly when memory other than graphics (chip) memory is present in the Amiga system. In this case, double-clicking on the NoFastMem icon forces the Amiga to use only the available graphics memory. The other mem display in the Workbench title bar drops to 0 (zero). The icon works like a toggle switch. To restore expansion (Fast) memory to the system, double-click on the NoFastMem icon again. NoFastMem does not open a window.
Python Drawer
This drawer contains the Amiga Python programming language.
Python is a powerful and easy to learn programming language. It has efficient high-level data structures and a simple but effective approach to object-oriented programming. It is an ideal language for scripting and rapid application development.
Python Interpreter
Python programs are stored in source code form and they are executed with Python interpreter Python.
Running Python Programs
The Python command is used to run a Python program. For example, to run a program called "hello.py" enter the following command in Shell:
python hello.py
If the "hello.py" file has execute and script file protection flags set, you can just type
hello.py
and Shell will execute the program using the Python interpreter.
Using Python Interactively
You can use Python interactively, too. Just double-click the Python tool icon in the Python drawer and an Amiga Python console window will open.
You can type any Python command in the console and it will be executed once you press Enter. To leave the interactive command mode, type exit() and press Enter.
Lib Drawer
This drawer contains the Python standard library.
The library contains built-in modules that provide access to system functionality such as the file I/O that would otherwise be inaccessible to Python programmers, as well as modules written in Python that provide standardized solutions for many problems that occur in everyday programming.
RexxMast
RexxMast is the interpreter for the optional ARexx programming language. If the RexxMast icon is not present, you do not have ARexx on your system. To use RexxMast, double-click on its icon. To run RexxMast each time you boot, drag the icon into WBStartup.
RinghioServer
RinghioServer is a desktop notification system. It allows applications to display notifications without interrupting the user. Ringhio displays a notification on the screen in a box. Depending on the notification priority, the notification box stays on the screen until it is clicked or, if it is a low priority notification, it disappears after a while.
See Chapter 5. Preferences on how to customize the notification system.
Shell
Shell opens an Amiga Shell window, which gives you complete access to the AmigaDOS command line environment.
TypeManager
Font installer.
Utilities Drawer
The Utilities drawer contains programs that are helpful, but not necessary for working with your Amiga.
AmiGS
AmiGS is a viewing and printing utility for postscript, EPS, and PDF documents.
Tool Types
AmiGS supports the following Tool Types:
| WINDOWBOX=<left>/<top>/<width>/<height> | This tool type allows you to define AmiGS window position and dimensions. |
| PUBSCREEN=<public screen> | Name of the public screen. AmiGS will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this tool type. |
Shell Usage
- Format
- AMIGS [FILE <file name>] [PAGE <page number>] [PAGENAME <page name>] [ZOOM <zoom factor>] [PUBSCREEN <public screen name>] [FULLSCREEN]
- Template
- FILE,PAGE/N,PAGENAME/K,ZOOM/K,PUBSCREEN/K,FULLSCREEN/S
ARexx Interface
AmiGS has an ARexx interface which allows other programs to control AmiGS while it is running. AmiGS's ARexx port name is AMIGS.<slot #>, where <slot #> is the ARexx port slot. When you have one AmiGS running, its ARexx port is AMIGS.1. The other instance of AmiGS has a port named AMIGS.2, the third instance AMIGS.3 and so on.
AmiGS upports the following ARexx commands:
| GETDEFAULTID | Returns the default document ID in the ARexx variable RESULT.
AmiGS creates a unique ID number for each opened document. The first opened document will get this ID number. AmiGS generates a new document ID by adding 1 to the last used ID number. Thus the second document's ID number will be 2, third's 3, and so on. When you close a document, its ID number won't be reused. |
| QUIT | Quits the application. |
| OPEN [<file name>] | Opens the named file in a new window or if the file name is not supplied, displays a file requester for selecting a file. |
| CLOSE <document id> | Closes an open document using the AmiGS's internal document ID number. |
| FIRSTPAGE <document id> | Displays the first page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| LASTPAGE <document id> | Displays the last page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| PREVPAGE <document id> | Displays the previous page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| NEXTPAGE <document id> | Displays the next page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| GOTOPAGE <document id> <page number> | Displays the requested page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
AmiPDF
AmiPDF is a PDF document viewer. It can also be used for converting PDF documents to text files and PostScript files.
Tool Types
AmiPDF supports the following Tool Types:
| WINDOWBOX=<left>/<top>/<width>/<height> | This tool type allows you to define AmiPDF window position and dimensions. |
| PUBSCREEN=<public screen> | Name of the public screen. AmiPDF will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this tool type. |
Shell Usage
- Format
- AMIPDF [FILE <filename>] [PAGE <page number>] [PAGENAME <page name>] [OWNERPASS <password>] [USERPASS <password>] [ZOOM <zoom factor>] [PUBSCREEN <public screen name>] [FULLSCREEN] [PAPERSIZE <paper size>] [PAPERWIDTH <paper width>] [PAPERHEIGHT <paper height>] [PSLEVEL1] [TEXTENCODING <encoding> ] [QUIET]
- Template
- FILE,PAGE/N,PAGENAME/K,OWNERPASS/K,USERPASS/K,ZOOM/K,PUBSCREEN/K,FULLSCREEN/S,PAPERSIZE=PS/K,PAPERWIDTH=PW/K,PAPERHEIGHT=PH/K,PSLEVEL1/S,TEXTENCODING=TE/K,QUIET/S
| FILE | Name of the PDF file to open. |
| PAGE | Page number. Open the PDF document from the specified page. |
| PAGENAME | Like PAGE except you can use page names instead of page numbers. |
| OWNERPASS | Document's owner password. Providing this will bypass all security restrictions. |
| USERPASS | Document's user password. As a minimum this will unlock the read protection. |
| ZOOM | Initial zoom factor. Percentage value. |
| PUBSCREEN | Name of the public screen. AmiPDF will open its window on the public screen which name has been supplied with this argument. |
| FULLSCREEN | Display the PDF document using the full-screen mode. |
| PAPERSIZE | Paper size: LETTER, LEGAL, A4, or A3. |
| PAPERWIDTH | Set the paper width in points. |
| PAPERHEIGHT | Set the paper height in points. |
| PSLEVEL1 | Generates Level 1 PostScript. The resulting PostScript file will be significantly larger (if it contains images), but will print on Level 1 printers. This also converts all images to black and white.
By default AmiPDF generates Level 2 PostScript. |
| TEXTENCODING | Sets the encoding to use for text output. |
| QUIET | Don't print any messages or errors. |
ARexx Interface
AmiPDF has an ARexx interface which allows other programs to control AmiPDF while it is running. AmiPDF's ARexx port name is AMIPDF.<slot #>, where <slot #> is the ARexx port slot. When you have one AmiPDF running, its ARexx port is AMIPDF.1. The other instance of AmiPDF has a port named AMIPDF.2, the third instance AMIPDF.3 and so on.
AmiPDF supports the following ARexx commands:
| GETDEFAULTID | Returns the default document ID in the ARexx variable RESULT.
AmiPDF creates a unique ID number for each opened document. The first opened PDF document will get this ID number. AmiPDF generates a new document ID by adding 1 to the last used ID number. Thus the second document's ID number will be 2, third's 3, and so on. When you close a document, its ID number won't be reused. |
| QUIT | Quits the application. |
| OPEN [<pdf file>] | Opens the named PDF file in a new window or if the file name is not supplied, displays a file requester for selecting a file. |
| CLOSE <document id> | Closes an open PDF document using the AmiPDF's internal document ID number. |
| FIRSTPAGE <document id> | Displays the first page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| LASTPAGE <document id> | Displays the last page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| PREVPAGE <document id> | Displays the previous page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| NEXTPAGE <document id> | Displays the next page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
| GOTOPAGE <document id> <page number> | Displays the requested page of the document which ID number is <document id>. |
Calculator
Clock
Clock displays the time and date on your Workbench screen. It can also be used as an alarm clock to signal you at a specified time.
When you open the Clock icon, a window with a round (analog) clock face appears. If the time Shown is incorrect, use the Time editor in the Prefs drawer, described in Chapter 5, to set the correct time.
Clock has two menus for changing the display and settings: Project and Settings.
The Project menu contains the following items:
| Analog | Displays the round Clock face. Analog is the default; its window size can be changed. |
| Digital | Displays a digital (numeric) clock the height of the title bar using your screen font. |
| Quit | Closes the Clock. |
The Settings menu contains the following items:
| Date | Displays the date beneath the analog clock. The date and time are alternately displayed on the digital clock. Date off is the default. |
| Seconds | Displays the time with a sweep second hand on the analog clock. The default setting shows no seconds. The Display Seconds item is overridden by the Digital Format setting when using the digital clock. |
| Digital Format | Displays the time in a 12 or 24 hour format, with or without seconds, for the digital clock only. |
| Alarm | Allows you to turn the alarm on or off. A checkmark indicates that the alarm is on. |
| Set Alarm | Allows you to set the time for the alarm to signal you. Because the signal is a short audible tone, you must have audio output on your Amiga to use this feature. |
| Save Settings | Saves your Clock settings. Each time you run the Clock program it opens with these settings until you change them. |
To set the alarm:
- Choose the Set Alarm menu item.
- Change the time setting by dragging the hour and minute sliders to the right to increase the value or the left to decrease the value until the correct time is displayed.
- When the requester displays the desired alarm time, select the Use gadget. This automatically turns the alarm on, as indicated by the checkmark next to the Alarm menu item. Select the Cancel gadget to restore the previous alarm setting and exit.
The alarm remains on and beeps at the same time each day until you deselect Alarm or close the Clock. The Clock must be running for the alarm to work. The next time you open the Clock, the alarm must be reset.
Tool Types
Tool Types in the Clock icon's Information window allow you to save the menu, size, and position settings on the Clock. The Clock's Tool Types are the same as its keywords in AmigaDOS.
More
More displays ASCII text filers on the Workbench screen. More does not have an icon, although it resides in the Utilities drawer. More has been superseded by the MultiView program (described on page 4-23), but is retained for compatibility with files that use More as their Default Tool.
The following key sequences can be used to move through the More display and to get help for using More:
| Space bar or down arrow | Displays the next page. |
| Backspace or up arrow | Displays the previous page. |
| H | Help (displays a list similar to this one). |
When the last page of the display is reached, an End of File message is displayed at the bottom of the screen. Press the space bar at this point or click the close gadget at any time to exit More.
GraphicDump
IconEdit
InitPrinter
Installation Utility
KeyShow
MEmacs
MultiView
MultiView lets you view files, including picture files, text files, AmigaGuide help files, sound files, and animated graphics files. It can display any type of file for which there is a data type file in DEVS:DataTypes. For more information on the data types used by MultiView, see page 4-28.
MultiView uses a standard file requester for loading files. You can load files into MultiView using the file requester provided or, because the MultiView window is an AppWindow, you can drag icons onto MultiView to load them.
When you loaded a standard Amiga sampled sound file into MultiView, clicking on the file's icon plays the sampled sound if your Amiga or monitor has speakers.
When you load an animated file into MultiView, the window or screen on which the animation is displayed has a control panel for manipulating the display. The control panel gadgets allow you to start and stop the animation and move forward or backward through it. This screen is illustrated in Figure 4-6.
MultiView has four menus: Project, Edit, Windows, and Settings.
Project Menu
| Open | Brings up a file requester to allow you to choose another file to display. |
| Save As | Saves object as ILBM or text files. |
| Prints selected blocks or files. | |
| About | Shows the MultiView release information and the type of document being viewed. |
| Quit | Quits MultiView. |
Edit Menu
| Mark | Turns on the block selection cursor and lets you select a block. (This is only available for picture files.) |
| Copy | Copies selected block to the Clipboard and deselects the block. If no block is selected, copies the whole file. |
| Select All | Selects the whole file. |
| Clear Selected | Clears the selected block or file without copying or printing. |
Windows Menu
| Use Separate Screen | Toggles between displaying the file on its own screen and in a window on the Workbench screen. |
| Minimize | Make the window as small as it can be. |
| Normal | Sizes the window to the contents size. |
| Maximize | Makes the window the same size as the screen. |
Settings Menu
| Save As Defaults | Saves the size, position, and location of the window for future use. |
Tool Types
MultiView supports the following Tool Types:
| CLIPBOARD | View The Clipboard instead of the file. |
| CLIPUNIT=<number> | Specify the Clipboard unit to use when using the CLIPBOARD keyword. The range is 0 to 255; the default is 0. |
| SCREEN | Indicate that you want the object to appear on its own screen, using the environment specified by the object. For example, if an ILBM was Low Res, then the screen would match. |
| PUBSCREEN=<name> | Indicate that you want the window to open on the named public screen. |
| FONTNAME=<name> | Font to use when viewing text objects. Note that the .font extension must be left off. |
| FONTSIZE=<number> | Font size to use when viewing text objects. |
| BOOKMARK | Go to the object and position specified by the bookmark. |
| BACKDROP | Indicate that the window should be a backdrop window. |
| WINDOW | Open the MultiView window on the Workbench screen without an object so that items can be dragged into it. |
| PORTNAME=<ARexx port name> | Allows you to specify an ARexx port name when you run MultiView. This name allows you to refer to a particular MultiView display from within an ARexx script. If no name is specified, each MultiView invocation is given a default name. |
For more information on using MultiView with ARexx, see the AmigaDOS User's Guide.
NotePad
Project Menu
Edit Menu
Settings Menu
PartitionWizard
Project Menu
Tools Menu
PlayCD
PrefsObjectsEditor
PrefsObjectsEditor Menu
PrintFiles
RawDisk
ShowConfig
UnArc
Project Menu
USBInspector
Project Menu
Internet Drawer
Emulation Drawer
WBStartup Drawer
The WBStartup drawer is provided to hold icons for programs that you want opened at the time the Workbench is started. For example, you may want the Clock program running when you reboot or power on your Amiga. Drag the icon for each desired program into the WBStartup window. The WBStartup drawer is empty by default.
Tool Types
Programs in the WBStartup drawer can include the following Tool Types:
| DONOTWAIT | Normally the Workbench waits for one program to finish before it opens the next. DONOTWAIT overrides this, which can cause unwanted requesters after booting. DONOTWAIT does not take an argument. |
| WAIT=<seconds> | Specifies how many seconds the Workbench should wait before opening the next icon in the WBStartup drawer. |
| STARTPRI=<priority> | Assigns a priority to an icon so that it opens before or after other icons. By default, all icons have a priority of 0. The acceptable range is from -128 to +127; the higher the value, the higher the program's priority. |
Expansion Drawer
The Expansion drawer is used to store software drivers for additional hardware devices that you install on your Amiga. If a hardware device uses the Expansion drawer, it is explained in the documentation packaged with that product. To activate the new device, drag the icon for the device's software driver into the Expansion drawer and then reboot your system to make the device available.
Devs Drawer/Storage Drawer
The Devs and Storage drawers both contain the following subdrawers:
- DataTypes
- DOSDrivers
- Keymaps
- Monitors
- Printers
| Note |
|---|
| Floppy disk-only systems use either the Storage disk or Storage drawer found in the software floppy disk set. |
The Devs drawer contains the device files for the devices that are currently active on the system. The Storage drawer or disk is for device driver files that are not currently in use. Storing unused files in the Storage drawer or disk can save disk space on your boot disk and reduces clutter in Preferences editor windows.
To activate a monitor or DOS driver:
- Double-click on the icon. The file is then active during the current session only.
- To have the icon active in all sessions, drag it from the Storage drawer into the corresponding Devs drawer and reboot your system.
To activate a keymap:
- Drag keymap files from the Storage drawer on the floppy disk into the Devs drawer.
- Select the appropriate Keyboard Type in the Input Preferences editor.
To activate a printer driver:
- Drag printer files from the Storage drawer on the floppy disk into the Devs drawer.
- Select the appropriate Printer Type in the Printer Preferences editor.
Data Types
Data types are software files used by tools, utilities, editors, and applications. They are used to describe file formats to the system, such as picture files, sound files, and text files. The following default data types are included with the system software:
| 8SVX | IFF sound files |
| AmigaGuide | Amiga Help files |
| FTXT | IFF text files |
| ANIM | ANIM-format animation files |
| CDXL | CDXL-format animation files |
| ILBM | Bitmap picture files |
Adding data types from other applications into the Devs/DataTypes drawer makes them available for use by the Workbench, as well as the application. Add new data types by dragging them into the Devs/DataTypes drawer and double-clicking on them.
DOSDrivers
DOS drivers are software drivers that extend the capabilities of AmigaDOS. The following DOSDrivers are included with the system software:
| PC0/PC1 | CrossDOS drivers for DF0: and DF1:, respectively (see Chapter 11 for details) |
| CD0 | CD-ROM driver (see below for details) |
| PIPE | Pipe driver (see the AmigaDOS User's Guide for details) |
| AUX | Auxiliary serial Shell driver (see the AmigaDOS User's Guide for details) |
| RAD | Recoverable RAM disk driver (see Appendix B for details) |
Using CD-ROM
CD-ROM drives allow you to read information from CD-ROM disks. When the CD0 device driver is activated, you can use the device name CD0: to refer to a connected CD-ROM. Refer to the documentation that came with your CD-ROM device for specific information about connecting and using the device with the Amiga.
To be sure that the CD-ROM drive works with your Amiga, you must determine the name of the device driver that provides the interface for the CF-ROM drive, typically scsi.device. You must also determine the unit number of the CD-ROM drive, which is included in the drive's documentation. The default device name is scsi.device and the default unit number is 2.
If your CD-ROM drive and interface device do not match the default, change the device name and the unit number to those appropriate for your CD-ROM drive as follows:
- Select the Execute Command item from the Workbench menu.
- Enter the following command and click on the OK button:
ED SYS:Storage/DOSDrivers/CD0 - Replace the device name on the DEVICE = line with the appropriate device name for your drive.
- Replace the unit number on the UNIT= line with the appropriate unit number for your drive.
- Save your changes by selecting the Save item in the Project menu.
- Quit ED by selecting the Quit item in the Project menu.
Keymaps
Keymaps control how text characters are mapped into the Amiga keyboard. For any Keyboard Type other than the default American to be available in the Input Preferences editor, the keyboard's keymap must be in DEVS:Keymaps. A list of keyboards and their corresponding keymaps appears in the Input editor section of Chapter 5.
Monitors
The Devs/Monitor drawer and the Storage/Monitors drawer contain icons for the available monitor types that you can use on your system. For any monitor type other than the default (NTSC or PAL, depending on your country) to be available in the ScreenMode Preferences editor, the corresponding monitor driver must be in DEVS:Monitors. See Chapter 7 for more details on using monitors.
NetInterfaces
Printers
The Devs/Printers drawer holds your printer drivers. Printer drivers that have not been loaded onto your system are located in the Storage/Printers drawer within the software floppy disk set. On a floppy disk system Devs/Printers initially holds only the Generic printer driver. On hard drive systems, the printer drivers specified during installation are installed there.
Activating a printer driver that is not already in DEVS:Printers is the same for floppy and hard disk systems. To load a printer driver and use a printer with your Amiga:
- Open the Devs drawer on your Workbench disk.
- Insert your Storage disk or disk containing the Storage drawer and open the Printers drawer.
- Drag your printer's icon onto the Devs/Printers drawer icon. (For singly floppy systems, follow the messages to change disks.)
- Open the Printer Preferences editor.
- Select the appropriate printer type from the Printer Type field in the Printer editor window.
On hard drive systems, you can store unused printer drivers in the Storage/Printers drawer.
See Chapter 9 for more details on using printers and activating printer drivers.