Copyright (c) Hyperion Entertainment and contributors.
Difference between revisions of "AmigaOS Manual: AmigaDOS Additional Amiga Directories"
Steven Solie (talk | contribs) |
Steven Solie (talk | contribs) (→DEVS:) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
For more information on the .device files, see [[Devices|Amiga Devices]]. |
For more information on the .device files, see [[Devices|Amiga Devices]]. |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Other Files == |
||
| + | |||
| + | The following additional files are found in DEVS: |
||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" |
||
| + | | system-configuration || Holds certain Preferences configuration data needed when booting. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Postscript_init.ps || Holds information needed to initialize a PostScript printer when using PrinterPS. |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Using Mount Files or a MountList === |
||
| + | |||
| + | To access new devices, the Amiga must be informed when any are added. These may be physical devices, such as a tape drive, or software (logical) devices, such as a recoverable RAM disk. There are several ways to do this: |
||
| + | |||
| + | * Placing a driver in the Expansion drawer |
||
| + | * Placing a mount file in the DOSDrivers drawer |
||
| + | * Making an entry for the device in a MountList file and using the MOUNT command |
||
| + | |||
| + | A mount file represents a device, handler, or file system. Standard devices have their own mount file with icons in the DOSDrivers drawer in DEVS:. These are mounted automatically during the standard Startup-sequence. Alternatively, devices can use the MOUNT command to read a MountList entry that determines the characteristics of the device. |
||
| + | |||
| + | The need to use a MountList and the MOUNT command has been eliminated by the mount file method used in Amiga system software Release 2.1 and beyond. Rather than requiring a MountList file with entries for each device you want to mount, DEVS: now contains the DOSDrivers drawer, which holds a separate mount file or DOS driver for each device. The contents of a mount file are essentially the same as an individual MountList entry. |
||
| + | |||
| + | You can, however, continue to use a MountList to mount devices. Copy the MountList to DEVS: and remove any DOS drivers in the DOSDrivers drawers that have the same name as one of your MountList entries. (A mount file overrides a MountList entry of the same name.) |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Creating a MountFile or MountList Entry === |
||
| + | |||
| + | The following information on mount files also applies to MountLists, except as noted. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Mount files contain keywords describing the device, handler, or file system, as well as values for those keywords. Some keywords apply only to a filesystem or a handler. If a keyword is omitted, a default value is used. Be sure that the default value is appropriate for the device. |
||
| + | |||
| + | The following are rules for creating a mount file or MountList: |
||
| + | |||
| + | * The file must be a plain ASCII text file. |
||
| + | * The mount file name must be the name of the device; the name of a MountList should be MountList. |
||
| + | * Each entry in a MountList must start with the name of the device. Omit this for a mount file. |
||
| + | * Keywords are followed by an equals sign (=). |
||
| + | * Keywords must be separated by a semicolon or be placed on separate lines. |
||
| + | * Comments are allowed in standard C style (that is, comments start with /* and end with */). |
||
| + | * Each MountList entry must end with the # symbol. Omit this for a mount file. |
||
| + | |||
| + | When creating a new mount file or MountList entry, refer to the documentation that came with the device or start with an example of one for a similar device. Change or add only the necessary keywords. |
||
| + | |||
| + | The following table, lists keywords and their default values supported in a mount file or MountList and their functions. Default values are shown in angle brackets. |
||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" |
||
| + | ! Keyword !! Function |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Handler=<none> || A handler entry (for example, Handler = L:eque-handler). |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Ehandler=<none> || An environment handler entry. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | FileSystem=<none> || A file system entry (for example, FileSystem = L:CrossDosFileSystem). |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Device=<none> || A device entry (for example, Device = DEVS:mfm.device). This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for Device; you must supply a value. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Priority=<10> || The priority of the process; 5 is good for handlers, 10 for file systems. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Unit=<0> || The unit number of the device (for example, 0 for PC0:). |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Flags=<0> || Flags for OpenDevice (usually 0). |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Surfaces=<none> || The numbner of surfaces (2 for floppy devices, varies for hard drives). This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for Surfaces; you must supply a value. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | SectorsPerBlock=<none> || Defines the number of physical disk sectors in each logical block used by the file system. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | SectorsPerTrack=<none> || The number of blocks per track. This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for SectorsPerTrack; you must supply a value. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | SectorSize=<512> || Specifies the number of bytes in a block on the device. Most devices use a 512 byte block; however, some devices use other sizes (for example, CD-ROMs use 2048 bytes). |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Reserved=<2> || The number of blocks reserved for the boot block; should be 2. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Interleave=<0> || Interleave value; varies with the device. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | LowCyl=<none> || Starting cylinder to use. This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for LowCyl; you must supply a value. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | HighCyl_<none> || Ending cylinder to use. This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for HighCyl; you must supply a value. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Stacksize=<600> || Amount of stack allocated to the process. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Buffers=<5> || Number of initial 512-byte cache buffers. Increase this for higher disk performance if you have RAM to spare. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | BufMem Type=<3> || Memory type used for buffers; (0 and 1 = Any, 2 and 3 = Chip, 4 and 5 = Fast). |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Mount=<0> || See the description of ACTIVATE, which is a synonym for MOUNT. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | MaxTransfer=<0x7ffffff> || The maximum number of bytes transferred at one time with any file system. Use Max Transfer for compatibility with older hard drive systems. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Mask=<0xffffffff> || Address Mask to specify memory range that DMA transfers can use at one time with any file system. Use Mask for compatibility with older hard drive systems. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Glob Vec=<2> || A global vector for the process; -1 is no Global Vector (for C and assembler programs), 0 sets up a private GV; if the keyword is absent, the shared Global Vector is used. Omit this keyword for Amiga file system devices. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Startup=<none> || A string passed to the device, handler, or file system on startup as a BPTR to a BSTR. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Activate=<0> || If a positive value, ACTIVATE loads the device or handler immediately rather than waiting for first access. Synonymous with MOUNT. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | BootPri=<0> || A value that sets the boot priority of a bootable and mountable device. This value can range from -129 to 127. By convention, -129 indicates that the device is not bootable and is not automatically mounted. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | DosType=<0x444F5300> || Indicates the type of file system, giving hexadecimal ASCII codes for three letters and a concluding number as follows: |
||
| + | {| class="wikitable" |
||
| + | ! Value !! ASCII !! File System |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x444F5300 || DOS0 || Original (OFS) |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x444F5301 || DOS1 || FastFileSystem (FFS) |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x444F5302 || DOS2 || International Mode OFS |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x444F5303 || DOS3 || International Mode FFS |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x444F5304 || DOS4 || Directory caching International Mode OFS |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x444F5305 || DOS5 || Directory caching International Mode FFS |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | 0x4D534400 || MSD0 || MS-DOS |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Baud=<1200> || Serical device baud rate. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Control=<0> || Serial device word length, parity, and stop bits. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | | Forceload=<0> || Forces a file system to be loaded form disk even though a suitable entry is in the resource list. If 0 (the default), check the resource list before the disk. If 1, always load from disk. |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |||
| + | = S: Directory = |
||
| + | |||
| + | The S: directory is generally reserved for AmigaDOS and ARexx scripts. However, you may place non-script files in S: or place script files in other directories. In addition to the Startup-sequence file, the User-startup file that you create, and Shell-startup files, the S: directory also contains teh scripts described in this section. |
||
Revision as of 23:13, 29 January 2014
In addition to the AmigaDOS commands, there are other files and directories on your Workbench disk. This chapter includes the following:
- DEVS:
- S:
- L:
- FONTS:
- LIBS:
- REXX:
- LOCALE:
- ENVARC:
- ENV:
- CLIPS:
- T:
- Classes
- C:
The drawers contained in DEVS: are described in the Workbench User's Guide .
You do not need a detailed understanding of the contents of the directories listed here. Unless specifically directed otherwise, you can safely ignore them. However, you should know their purposes and locations in case you inadvertently delete or rename a file in a directory or need to copy something to the appropriate directory.
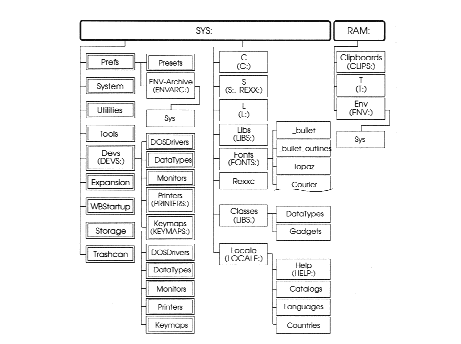
Figure B-1 illustrates the standard directory structure of a hard disk Amiga system. Directories with icons visible from Workbench (drawers) are shown on the left; other directories are on the right. The standard contents and structure of these directories may change as Commodore adds, changes, or removes resources.
Most of these directories are automatically assigned to the SYS: volume or to the Ram Disk. These directories, as well as SYS:, can be ASSIGNed to different volume when necessary.
For example, you can assign FONTS: to a particular disk, such as FontDisk:. Most applications automatically look for the fonts that they need in the FONTS: directory, regardless of where that is. By changing the FONTS: assignment, you can allow applications to use the fonts on FontDisk:
Contents
DEVS:
In addition to the DOSDrivers, Keymaps, Printers, Monitors, and DataTypes drawers described in the Workbench User's Guide, the DEVS: drawer contains files and subdirectories that pertain to the devices that can be used with the Amiga.
Note that you can refer to the DEVS:Keymaps and DEVS:Printers drawers by their assigned names KEYMAPS: and PRINTERS:, respectively.
Device Files
The following lists the .device files in DEVS: and their functions:
| clipboard.device | Controls access to CLIPS:. |
| Parallel.device | Controls access to the parallel port. |
| printer.device | Controls access to the printer device. |
| Serial.device | Controls access to the serial port. |
| mfm.device | Controls access to MS-DOS disks with CrossDOS. |
For more information on the .device files, see Amiga Devices.
Other Files
The following additional files are found in DEVS:
| system-configuration | Holds certain Preferences configuration data needed when booting. |
| Postscript_init.ps | Holds information needed to initialize a PostScript printer when using PrinterPS. |
Using Mount Files or a MountList
To access new devices, the Amiga must be informed when any are added. These may be physical devices, such as a tape drive, or software (logical) devices, such as a recoverable RAM disk. There are several ways to do this:
- Placing a driver in the Expansion drawer
- Placing a mount file in the DOSDrivers drawer
- Making an entry for the device in a MountList file and using the MOUNT command
A mount file represents a device, handler, or file system. Standard devices have their own mount file with icons in the DOSDrivers drawer in DEVS:. These are mounted automatically during the standard Startup-sequence. Alternatively, devices can use the MOUNT command to read a MountList entry that determines the characteristics of the device.
The need to use a MountList and the MOUNT command has been eliminated by the mount file method used in Amiga system software Release 2.1 and beyond. Rather than requiring a MountList file with entries for each device you want to mount, DEVS: now contains the DOSDrivers drawer, which holds a separate mount file or DOS driver for each device. The contents of a mount file are essentially the same as an individual MountList entry.
You can, however, continue to use a MountList to mount devices. Copy the MountList to DEVS: and remove any DOS drivers in the DOSDrivers drawers that have the same name as one of your MountList entries. (A mount file overrides a MountList entry of the same name.)
Creating a MountFile or MountList Entry
The following information on mount files also applies to MountLists, except as noted.
Mount files contain keywords describing the device, handler, or file system, as well as values for those keywords. Some keywords apply only to a filesystem or a handler. If a keyword is omitted, a default value is used. Be sure that the default value is appropriate for the device.
The following are rules for creating a mount file or MountList:
- The file must be a plain ASCII text file.
- The mount file name must be the name of the device; the name of a MountList should be MountList.
- Each entry in a MountList must start with the name of the device. Omit this for a mount file.
- Keywords are followed by an equals sign (=).
- Keywords must be separated by a semicolon or be placed on separate lines.
- Comments are allowed in standard C style (that is, comments start with /* and end with */).
- Each MountList entry must end with the # symbol. Omit this for a mount file.
When creating a new mount file or MountList entry, refer to the documentation that came with the device or start with an example of one for a similar device. Change or add only the necessary keywords.
The following table, lists keywords and their default values supported in a mount file or MountList and their functions. Default values are shown in angle brackets.
| Keyword | Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handler=<none> | A handler entry (for example, Handler = L:eque-handler). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ehandler=<none> | An environment handler entry. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FileSystem=<none> | A file system entry (for example, FileSystem = L:CrossDosFileSystem). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Device=<none> | A device entry (for example, Device = DEVS:mfm.device). This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for Device; you must supply a value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Priority=<10> | The priority of the process; 5 is good for handlers, 10 for file systems. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unit=<0> | The unit number of the device (for example, 0 for PC0:). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flags=<0> | Flags for OpenDevice (usually 0). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surfaces=<none> | The numbner of surfaces (2 for floppy devices, varies for hard drives). This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for Surfaces; you must supply a value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SectorsPerBlock=<none> | Defines the number of physical disk sectors in each logical block used by the file system. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SectorsPerTrack=<none> | The number of blocks per track. This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for SectorsPerTrack; you must supply a value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SectorSize=<512> | Specifies the number of bytes in a block on the device. Most devices use a 512 byte block; however, some devices use other sizes (for example, CD-ROMs use 2048 bytes). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reserved=<2> | The number of blocks reserved for the boot block; should be 2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interleave=<0> | Interleave value; varies with the device. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LowCyl=<none> | Starting cylinder to use. This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for LowCyl; you must supply a value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HighCyl_<none> | Ending cylinder to use. This argument is required to mount a file system. There is no default value for HighCyl; you must supply a value. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stacksize=<600> | Amount of stack allocated to the process. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffers=<5> | Number of initial 512-byte cache buffers. Increase this for higher disk performance if you have RAM to spare. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BufMem Type=<3> | Memory type used for buffers; (0 and 1 = Any, 2 and 3 = Chip, 4 and 5 = Fast). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mount=<0> | See the description of ACTIVATE, which is a synonym for MOUNT. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MaxTransfer=<0x7ffffff> | The maximum number of bytes transferred at one time with any file system. Use Max Transfer for compatibility with older hard drive systems. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mask=<0xffffffff> | Address Mask to specify memory range that DMA transfers can use at one time with any file system. Use Mask for compatibility with older hard drive systems. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glob Vec=<2> | A global vector for the process; -1 is no Global Vector (for C and assembler programs), 0 sets up a private GV; if the keyword is absent, the shared Global Vector is used. Omit this keyword for Amiga file system devices. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Startup=<none> | A string passed to the device, handler, or file system on startup as a BPTR to a BSTR. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activate=<0> | If a positive value, ACTIVATE loads the device or handler immediately rather than waiting for first access. Synonymous with MOUNT. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BootPri=<0> | A value that sets the boot priority of a bootable and mountable device. This value can range from -129 to 127. By convention, -129 indicates that the device is not bootable and is not automatically mounted. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DosType=<0x444F5300> | Indicates the type of file system, giving hexadecimal ASCII codes for three letters and a concluding number as follows:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Baud=<1200> | Serical device baud rate. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Control=<0> | Serial device word length, parity, and stop bits. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forceload=<0> | Forces a file system to be loaded form disk even though a suitable entry is in the resource list. If 0 (the default), check the resource list before the disk. If 1, always load from disk. |
S: Directory
The S: directory is generally reserved for AmigaDOS and ARexx scripts. However, you may place non-script files in S: or place script files in other directories. In addition to the Startup-sequence file, the User-startup file that you create, and Shell-startup files, the S: directory also contains teh scripts described in this section.